Category Archives: Styles
Fun Blends: Fifty Shades of Earl Grey

At the height of popularity of the Fifty Shades of Grey books, we still owned a combo bookstore and tea bar. I was working on some Earl Grey recipes, and thought it would be fun to do a Fifty Shades parody since the books were still selling well. It was just for fun, and I didn’t think it would earn a permanent spot on our tea menu, but this odd blend became one of our top sellers.
DISCLAIMER: There is no connection whatsoever between this tea and the Fifty Shades of Grey books. This is not a licensed product, and it has not been endorsed or authorized. It is strictly a parody.
The tea is based on a Kenyan black tea with a bit of Ceylon and purple tea mixed in. Then, of course, it gets the bergamot oil that characterizes an Earl Grey—a lot of bergamot. On top of that is a melange of cinnamon, orange, lemongrass, cornflower petals, and other goodies. Some of the ingredients were added for flavor, and some for looks. I wanted a black & blue tea, and I wanted something with a dominating flavor. What can I say? I just couldn’t resist the wordplay.
Coincidentally, it’s certainly one of the prettiest teas we have. People couldn’t resist the tea shot through with color, especially the cornflower petals, which added nothing whatsoever to the taste.

The Logo
After a variety of local artists had been having the fun of producing logos for our house blends, I thought it was about time to do another one myself. Since drawing isn’t my strong suit, I decided to pick a blend where I could work from a stock photo to start, and Fifty Shades of Earl Grey would be a good one to start with.
For the background picture, I wanted to capture the feel of the book cover artwork without using any of their imagery. I found a stock photo I liked, clipped out a portion of the pot with the steam, extended the dark background, and then adjusted the tone to get that bluish-grey color we ended up with. For the text, I chose a typeface with the look & feel of an old typewriter font, but proportionately spaced, and then I kerned it to suit.
The tagline at the bottom? Well, once again, I just couldn’t resist.
What’s the difference between Japanese and Chinese green tea?
As I did last month and the month before, I took a look at some of the search terms that brought people to this blog and found a question that I didn’t really address. This time: “What’s the difference between Japanese and Chinese green tea?” The obvious smart-aleck answer is that one comes from Japan and the other comes from China, but it runs a bit deeper than that.
First off, it’s not the plants themselves. The first varietal discovered of the tea plant is Camellia sinensis var. sinensis: the Chinese tea plant. About 1400 years ago, during the Sui Dynasty, Buddhist monks introduced tea — and the tea plant — to Japan. This means that the same varietal of tea plant is growing in China and Japan.
Terroir, on the other hand, can definitely have an effect. The climate, soil, and other factors can definitely affect the taste of the tea. Also, the Japanese have been crossbreeding and developing their strains of tea plant for over a millennium.
The biggest factor in the taste, though, is a very simple one: the process.
The difference between black tea and green tea is oxidation. Black tea is fully (or near-fully) oxidized, while green tea is not oxidized at all. There is an enzyme in the tea leaf that starts the oxidation process as soon as the leaf has been broken or bruised. Making green tea requires a “kill green” step that destroys the enzyme and stops the tea from oxidizing. That step requires heating the tea leaves quickly to at least 140 degrees.
To make Japanese green teas, such as sencha, bancha, and gyokuro, the leaves are steamed. To make Chinese green teas, such as dragonwell or gunpowder tea, the leaves are pan-fired. Just this simple difference in processing gives Japanese teas a rich grassy flavor and Chinese greens more of a vegetal character.
Granted, I am oversimplifying, but this is the fundamental answer to the question.
Old familiar blends vs. creative house blends

It’s a dilemma for anyone who owns or manages a tearoom: how many different teas shall I carry and how many of them should be funky house blends? Looking at last year’s sales, our top four sellers were very traditional teas: an earl grey, a breakfast blend, a masala chai, and a Moroccan mint (note that only one of those is unflavored). The next six were all creative flavored teas.
Reading that may make you think that the classics aren’t important for the tea bar, but let’s look behind those numbers:
First of all, those only reflect our bulk tea sales, not sales by the cup. I don’t have a good system in place for tracking sales by the cup—especially since we make some special by the cup blends for our regulars—but I’d guess that a lot more of our cup sales are straight traditional tea than the bulk numbers indicate. When I’m behind the bar, I sell a lot of Darjeeling, assam, sencha, silver needle, dragonwell, Scottish breakfast, jasmine green, taiguanyin, and shu pu-erh by the cup.
Second, those numbers include web sales. On the web, there are many many sources for sencha or Darjeeling, and we compete against the huge Internet retailers who can undercut our prices. On the other hand, there is only one source for our house blends like Mr. Excellent’s Post-Apocalyptic Earl Grey or Coyotes of the Purple Sage. We sell very little dragonwell on the web site compared to our house blends.
When deciding what tea to carry in your shop, the first thing to ask yourself is, who is your target audience? If you want to capture the Celestial Seasonings fan, you want to have a lot of flavored blends with colorful logos and clever names. If you want to capture the serious tea fan, you’d better have a good selection of unflavored tea of various styles and origins.
Of the styles, a casual shop would be expected to have black and green at the very least, with at least one white and one oolong. A more serious shop should expand the oolong selection significantly and add a couple more white teas and at least one or two pu-erhs. The sign of a teahouse that really caters to the connoisseur would be an extensive collection of ripe (shu) and raw (sheng) pu-erh in both loose and cake form, and a yellow tea or two.
When it comes to origins, a shop can go two different ways: specialized or generalized. It’s easy to put together a tea selection covering every style if all of the tea comes from China. It’s possible to cover the four basic styles from countries like India and Kenya, although the selection of oolongs and whites will be pretty sketchy. In my opinion, a generalized shop should have tea from, at the very least, China, Japan, Taiwan, India, Kenya, and Sri Lanka.
If you are going to offer house blends, I’ve found that they do best with unique names, preferably tied to your theme or location. Your customers can find English Breakfast and Moroccan Mint anywhere, and many would argue that you should use exactly those names so that your customers can find something familiar. On the other hand, hearty adventurers who find a tea shop in New York offering Buffalo Breakfast and Manhattan Mint are likely to come back for more if they like it instead of just grabbing generic English Breakfast and Moroccan mint at the next store they see.
You’ll want to offer some caffeine-free alternatives as well. It’s a philosophical decision whether you want to offer decaffeinated tea, naturally caffeine-free alternatives (e.g., rooibos), or both. Lately, we have a lot more customers specifically looking for rooibos. Most of them want flavored blends, but there’s enough demand to keep plain organic red and green rooibos available as well.
The bottom line is that your tea shop should reflect your personality. If people want a drab corporate-looking shop, they’ll go to Teavana. An independent tearoom should be unique, and the tea selection is even more important than the decor in conveying that uniqueness.
Fun Blends: Coyotes of the Purple Sage

With new tea blends, sometimes we come up with the tea first and struggle to think of the perfect name. Sometimes we come up with a cool tea name and then spend weeks tweaking the formula until we find just the right taste. And then the logo works its way into the equation.
Sometimes, however, everything comes together in a flash, and that’s what happened with this tea.
We were looking for ideas for a fundraiser, using a tea that had a real American West flavor to it. Being a tea bar/bookstore combo, a literary allusion makes things even better. As we were throwing out ideas, someone said “Zane Grey.” The next obvious leap was “a Zane Grey Earl Grey.” The next obvious leap was to Zane Grey’s best-known book, Riders of the Purple Sage.
The ingredients for the tea came together pretty quickly as well. Black tea and bergamot oil are the base for most Earl Greys. Sage was pretty much a mandatory ingredient. A bit of lemon verbena and lemon thyme added more citrus notes and the thyme goes well with the sage (I will resist breaking into song here), and a subtle touch of peppermint finished off the blend.
The Logo
The fundraiser is for the Yellowstone Wildlife Sanctuary here in Red Lodge, and two of the well-known noisy critters right by the entrance are a pair of coyotes named Bonnie and Clyde. We wrapped everything up by tying in the Wildlife Sanctuary and naming the tea Coyotes of the Purple Sage.
My logo is an homage to the cover of the first copy of Riders of the Purple Sage that I read, shown in the banner at the top of this article.
Rooibos: The African Red Bush
How have I been at this blog for so long without writing about rooibos? Oh, I know this blog is about tea, and I did write a post about green rooibos last year, but I haven’t covered straight red rooibos yet.
Rooibos comes from a bush called Aspalathus linearis, which grows in the west cape of South Africa. The name “rooibos” is from the Dutch word “rooibosch” meaning “red bush.” The spelling was altered to “rooibos” when it was adopted into Afrikaans.
Rooibos is also often called “red tea,” but most tea professionals shy away from that name for several reasons:
- The term “red tea” is used by the Chinese to refer to what we call “black tea.” No sense having two different drinks with the same name.
- Rooibos isn’t tea, since it doesn’t come from the Camellia sinensis plant. Instead, it is a tisane or herbal infusion.
- Rooibos only has that rich red color when it’s processed like a black tea. Green rooibos is more of a golden honey-colored infusion.
 Rooibos is a tasty drink that is also good for cooking. Hopefully, I’ll have a chance sometime soon to write a review soon of the cookbook A Touch of Rooibos. I have been looking through it lately and it’s filled with interesting ideas. Generally, when used for cooking, the rooibos is steeped for quite a while and then reduced to a thick syrupy consistency. Unlike black tea, it can be steeped for ten minutes or more without becoming unpalatable and bitter.
Rooibos is a tasty drink that is also good for cooking. Hopefully, I’ll have a chance sometime soon to write a review soon of the cookbook A Touch of Rooibos. I have been looking through it lately and it’s filled with interesting ideas. Generally, when used for cooking, the rooibos is steeped for quite a while and then reduced to a thick syrupy consistency. Unlike black tea, it can be steeped for ten minutes or more without becoming unpalatable and bitter.
Unlike “real” tea, which all has caffeine, rooibos is naturally caffeine-free. Since the flavor is similar to a mild black tea, this makes it a favorite bedtime beverage for many tea drinkers. Rooibos is also high in antioxidants.
Herbalists make many claims about the health properties of the rooibos tisanes. The Web site for the South African Rooibos Council (SARC), in fact, has very little information that isn’t in some way tied back to health claims. There are more and more studies being done, but available data are lacking in specifics (in my opinion, anyway) so I’m not going to quote any of those there. Feel free to check SARC’s site for lots of studies.
I don’t mean to imply that rooibos is only about the health benefits. It is, in fact, a very tasty drink. Most rooibos drinkers in the U.S. enjoy it straight or with a bit of sweetener (honey or sugar). In South Africa, it is commonly served with a bit of milk or lemon as well as honey. A group funded by SARC and Stellenbosch University has recently developed a “sensory wheel” for rooibos, describing both the desirable and undesirable aspects of flavor and mouthfeel. If you are interested in more information, click on the wheel below.
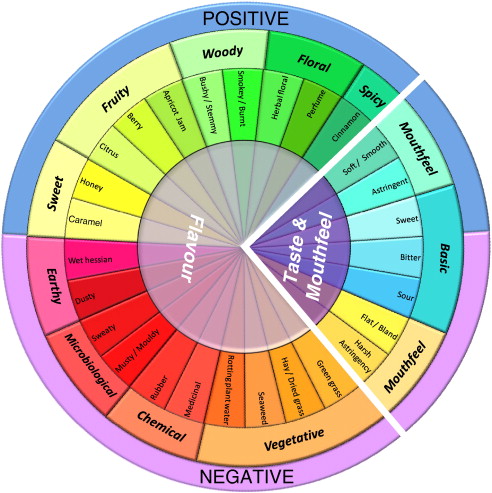
Rooibos Sensory Wheel as described in the article “Sensory characterization of rooibos tea and the development of a rooibos sensory wheel and lexicon,” available on Science Direct. Click the wheel above to view the article — there is a charge for the full text version.
 Also, there is an article you can download in PDF format (click the thumbnail to the right to download) that describes the sensory wheel and the process used to create it.
Also, there is an article you can download in PDF format (click the thumbnail to the right to download) that describes the sensory wheel and the process used to create it.
Compared to tea, rooibos is a pretty small market. South Africa’s annual rooibos production is about 12,000 tons. That output is about equivalent to annual tea production of the Darjeeling region of India, or about a tenth of the tea production of Japan (the 8th largest tea producing country). Nonetheless, rooibos is important to South Africa, employing about 5,000 people and generating about $70 million in revenues.
The leaves of the rooibos bush are more like needles than the broad leaves of a tea plant. To produce red rooibos, the leaves are harvested, crushed, and oxidized using a process based on the one used in making Chinese black tea. Typically, the leaves are sprayed with water and allowed to oxidize for about 12 hours before being spread out in the sun to dry.
Green rooibos, as the name implies, is unoxidized or very lightly oxidized, and is processed more like a green tea.
For more information about the rooibos industry, I recommend the article Disputing a Name, Developing a Geographical Indication, from the World Intellectual Property Organization.
The Lady Greystoke logo
Does it seem like I’ve got a theme going on this blog lately? I’ve had quite a few posts about the fun we’ve been having with logos for our house blend teas. Some great artist friends have done logos for us, including Al Jones (Hammer & Cremesickle Red Tea and Robson’s Honey Mint), Brandon Pope (Mr. Excellent’s Post-Apocalyptic Earl Grey), and Suzanna Bailey (MaterniTEA). Now, I’d like to introduce the latest in the series: Doug Bailey (Suzanna’s husband) made us a logo for our Lady Greystoke tea (the story behind the blend is here).
As with the other artists, I didn’t give Doug any direction at all beyond explaining the origin of the name and the ingredients in the blend. He picked up on the “wild yet civilized” aspect of Jane Greystoke, and being Doug (his nickname is “the Beerbarian”), he added a saber-toothed tiger. I don’t remember any saber-toothed tigers in the Tarzan books, but that’s probably just because Edgar Rice Burroughs didn’t think of it.
Doug is a pencil kind of guy, so he gave me the logo as a pencil sketch and I colorized it. I’ve always done my colorizing by scanning the image, loading it into Photoshop, making the background transparent, and then painting behind the image. This has the disadvantage of taking out light shading and fine detail from the original sketch, and Doug did a lot of shading in this one.
This time around, I added the color by creating new layers for each element (16 layers in this case) and setting the layer to a linear burn. That way, I don’t have to modify the original layer at all, and any shading—no matter how subtle—shows through the color.
As an aside, I’ve always preferred to drink my Earl Grey teas hot. I got to thinking about iced Earl Grey today when a customer ordered an iced Lady Greystoke at the Tea Bar, so I had to give it a try. The addition of the lavender, rooibos, and vanilla really seems to make this a smooth iced tea. I may be drinking more of it iced.
Fun Blends: MaterniTEA for Morning Sickness

I am a tea lover, not an herbalist. Let me repeat that for emphasis: I am not an herbalist. I am not trained in the healing powers of herbs (and I believe that most of the claims about most of the herbs are horse-hockey, but that’s another story), but I know what people ask for at the tea bar. We seem to have a lot of pregnant women in town these days, and most of them come in requesting either ginger or mint for their morning sickness.
I did some reading, and found that most of the published studies agree that those are two herbs that settle the stomach well. I know ginger works for me. Doing a straight ginger-mint blend, however, tasted pretty wretched. I started monkeying around with combinations—carefully avoiding caffeine—and came up with MaterniTEA. It uses green rooibos, Egyptian chamomile, and honeybush as its base, along with the aforementioned organic peppermint and ginger. A touch of orange extract for flavor, and we have something that tastes good as well as helping with the nausea that triggered this whole thing.
The Logo
This logo was drawn by the lovely and talented Suzanna Bailey.In keeping with the philosophy I described in the last tea label post, I didn’t give Suzanna any specific instructions. I just described the tea and threw out a few adjectives like “soothing” and “relaxing,” and got out of her way. She came back with several pages of ideas and sketches, and one of them really caught my eye. My wife, Kathy, and I absolutely loved the look of the steam rising from a teacup in the shape of a pregnant woman.
Suzanna has an amazing eye for color, so she did all of the drawing and the coloring for this one—she just asked if I could fill in the lettering. Once again I am thrilled with the results and we’re having posters made of all of our custom tea logos.
Thank you, Suzanna!
Yet another new logo: Mr. Excellent’s Post-Apocalyptic Earl Grey
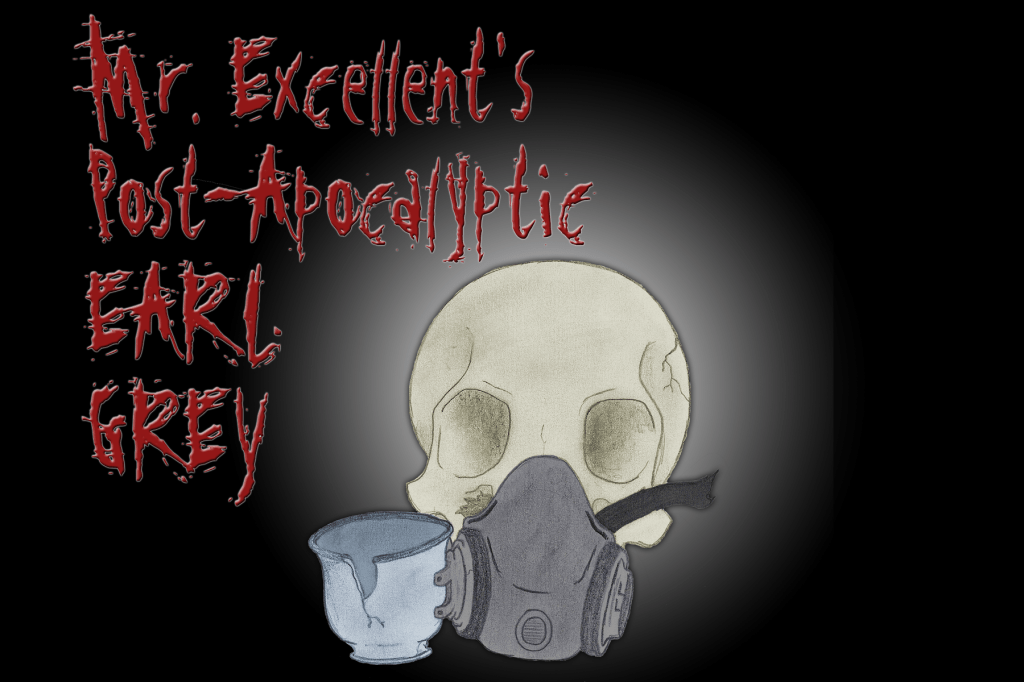
Such a delay! It was about eight months ago that I came up with the Mr. Excellent’s Post-Apocalyptic Earl Grey Tea blend (see my blog post about it here), and we finally have a logo for it! This one was drawn by my daughter’s friend from college, Brandon Pope.
I’ve found that logo art comes out better if I don’t tell the artist what I want, so I gave Brandon little more information than the name of the tea and what it is (an Earl Grey lapsang souchong). If I could draw, I probably would have done something with a dude sitting in the middle of a burned-out town, his shotgun at his side, drinking a cup of tea as the zombies eye him from a distance. In other words, something way too complex to use as a logo.
Brandon came up with the skull and gas mask, with one of the air filters replaced by a teacup. Very simple, yet immediately recognizable. His original was a hand-lettered pencil sketch (see below), which I needed to colorize. Brandon’s shading was great, especially where the texture of the paper showed, so I just added solid blocks of color behind the skull, mask, and teacup.
I really, really wanted to put this one on a black background, and I just couldn’t seem to make that work using his text. I re-did the text using a fun font called “Disgusting Behavior,” stretched vertically to achieve the look and aspect ratio that I was after. A blood-red color for the text with a subtle glow and an emboss effect finished it off perfectly.
For comparison, here is Brandon’s original pencil sketch (below) and the final logo (above). You can click on the final logo for a larger image.

This whole program of guest artists for tea logos (kicked off by Al Jones and his Hammer & Cremesickle logo) has been a blast. Thank you very much to Brandon for the artwork, and watch this space for guest logos by husband and wife team Doug and Suzanna Bailey, coming up soon.
Lady Greystoke

Enid Markey, the first actress to bring Jane Porter to life in film. Jane married Tarzan in the book, "The Return of Tarzan," becoming Lady Jane Greystoke.
As I mentioned a couple of days ago, we decided to rename our Lady Grey tea. I put the word out to friends on all of the social media, and a former fellow moderator at the Straight Dope Message Boards who goes by the moniker of “Czarcasm” came up with the winning suggestion: Lady Greystoke.
Since the tea bar is a part of Red Lodge Books, we liked the literary connection behind Lady Greystoke: In Edgar Rice Burroughs’ Tarzan books, Jane Porter was the love interest. Tarzan himself was John Clayton, Earl Greystoke, so when he married Jane in the second book of the series (The Return of Tarzan), she became Lady Greystoke.
We had many other great suggestions — and quite a few silly ones — but none caught our attention quite like this one. We just may use several of those other names for other blends in the future, so we appreciate everyone who took the time to make suggestions.
The most common suggestion, interestingly, was to call the tea Jane Grey. Lady Jane Grey, also known as The Nine Days’ Queen, was the great-granddaughter of Henry VII. She ruled as de facto Queen of England for nine days in 1553, and was later executed for high treason. Since Lady Greystoke was also a Jane, we liked this connection, too.
In celebration, I shall be enjoying a mug of Lady Greystoke tea tomorrow morning at the tea bar. Everyone’s invited to come in and join me!
Lady Grey
 Today was tea blending day at the tea bar, as I mixed up new batches of our house blends. As I was working on our Lady Grey, I got to thinking about how incredibly different Lady Grey teas are from one company to the next, and decided to do a bit of reading on the subject.
Today was tea blending day at the tea bar, as I mixed up new batches of our house blends. As I was working on our Lady Grey, I got to thinking about how incredibly different Lady Grey teas are from one company to the next, and decided to do a bit of reading on the subject.
It didn’t take long to find a comment that “Lady Grey” is a registered trademark of R. Twining and Company in the U.S. and U.K. (here’s a link to the trademark search on Trademarkia that shows it renewed in March of 2006). This hasn’t stopped quite a few companies from producing their own variations, like Jasmine Pearl (theirs has orange zest and lemon myrtle, but no bergamot!), SereneTeaz (an Earl Grey with lavender), American Tea Room (they don’t have a full ingredient list, but it includes cornflower petals), and Tea Embassy (another Earl Grey with lavender).
Should I follow their lead and continue calling my blend Lady Grey? Nah. I have better things to do with my time and money than fight legal battles. I’ll do the right thing and follow the example of Marks & Spencer (they call theirs Empress Grey) and Trader Joe’s (Duchess Grey).


Twinings originally named their Lady Grey tea for Mary Elizabeth Grey. Their Earl Grey tea (which they changed last year) was named for her husband, Charles, who was the second Earl Grey. Twinings uses less bergamot in their Lady Grey than they do in Earl Grey, but they add other citrus and some cornflower.
I’ve never understood the rationale of “clone blends.” My “Lady Grey” isn’t the same as anyone else’s. If it was, I’d just buy theirs. I want something different. Mine is an organic blend, using Chinese black tea, oil of bergamot, wild Tibetan lavender, a little bit of vanilla, and a touch of rooibos.
What to call it? The one consistent thing about all of our other Earl Grey teas is the word “Earl.” Earl Green (green tea + bergamot), Earl Red (rooibos + bergamot), and all of the blends that use the full “Earl Grey” moniker, like Mr. Excellent’s Post-Apocalyptic Earl Grey and Cream Earl Grey. The name “Lady Grey” keeps the “Grey” instead of the “Earl,” but is still connected.
So I have done what I often do in such situations: turn the question over to my friends, colleagues, and acquaintances. I’ve asked Facebook and the Twitterverse for suggestions, and I’m starting a thread on my favorite message board (the Straight Dope). When we decide on a new name, you’ll read about it here first!










