Blog Archives
Jasmine Tea
Even purists who eschew “flavored” teas will often enjoy a cup of jasmine green tea. Perhaps it is because when you look at the loose tea, all you see is tea leaves; there are no visible indications that your tea leaves have been adulterated in any way. Perhaps it is because the affect of the jasmine in a well-made jasmine tea is delicate and subtle. Perhaps it is the rich history of jasmine teas.
Jasmine first made its way to China from Persia (now known as Iran) over 1,700 years ago, and it took hundreds of years before it was used to scent tea. Even then, it spread quite slowly, and it wasn’t until the Qing Dynasty, which began in 1644, that it became widespread.
The making of jasmine tea is quite different from typical flavored teas. Most flavored teas are either blends, where dry ingredients are mixed together, or tea leaves sprayed with flavor extracts, like Earl Grey with its bergamot oil. Jasmine tea, on the other hand, is scented rather than flavored.
In the traditional process, jasmine flowers are picked early in the morning, when the blossoms are still tightly rolled. Trays of processed and dried tea leaves (usually, but not always, green tea) are stacked in alternation with trays of jasmine. The trays have woven mesh or screens as bottoms, so as the jasmine blossoms open up and release their scent, it travels freely into the tea leaves over the course of about four hours.

The tea leaves pick up moisture from the flowers along with the jasmine scent, so they have to be re-dried before they can be packaged. In the finest quality jasmine teas, this scenting process may be repeated half a dozen times or more. The finished tea has no jasmine blossoms in it — only the scent that has transferred.
How you prepare a cup of jasmine tea depends on the base tea used. If it is made form a green tea, as most of them are, then you’ll want to use 175-185°F (80-85°C) water, and steep for three minutes or less. Using boiling water is a quick way to ruin a good cup of jasmine tea — or any other green tea, for that matter — by bringing out unwanted bitterness.
Grades of jasmine tea vary with the quality of the tea and the process used. One of the popular higher-end styles involves tea leaves that are tightly rolled, often known as “jasmine pearls.”

When drinking jasmine pearls, seven balls are placed in a small cup. Seven is considered good luck, so with jasmine pearls you don’t weigh them out or measure them in a tablespoon. Each rolled ball contains two leaves attached to a bud, which will slowly unfurl when the hot water is added.
Unlike most loose tea, jasmine pearls are infused right in the cup with no screens or filters, and you don’t remove them before drinking. The unbroken leaves assure that if you sip carefully, you won’t get a mouthful of leaf. If you’re drinking jasmine pearls with friends, the host should make sure that there’s always more hot water available to keep refilling the cups.
Jasmine blossoms certainly aren’t the only flowers used to scent tea — I’ve written about Vietnamese Lotus Tea, for example — but jasmine is definitely the best-known and most popular.
Champagne, Tequila, Darjeeling, and Dark Tea

If you make a carbonated white wine, it’s called a “sparkling wine,” unless you are producing it in the Champagne region of France. Then, and only then, should it be called Champagne. I say “should” because there are a number of countries that didn’t sign (or don’t honor) the treaties involved, but that’s a whole different blog post.
The same applies to beverages made from distilling blue agave cactus. If you are in the Mexican state of Jalisco, or designated portions of certain other states, you may call that beverage Tequila. Otherwise, you have made mezcal.
The theory behind these distinctions is not so much the strict corporate trademark enforcement that governs most usage of names in the U.S. It is more a question of terroir. If you were to take two cuttings from the same grape vine and plant one in Napa Valley, California and the other in the Rhine Valley of Germany, you would get different wines from the two vines. Terroir describes the effect that the soil, weather, drainage, and related geographical factors have on the resulting taste of the beverage, whether it be wine or tea.
Darjeeling tea is often called the Champagne of tea (this appellation is usually reserved for first flush Darjeeling tea, but we’ll ignore that distinction for the moment). This little factoid has little to do with the subject of the article, but does make for a marvelous segue from alcoholic beverages to teas, n’est pas?
Like Champagne and Tequila, Darjeeling refers not only to a particular style of tea, but to the origin of that tea: the Darjeeling district of West Bengal, India. Darjeeling tea is unique because of its terroir, but also because of the varietal of the tea plant that they use. Most tea grown in India comes from Camellia sinensis var assamica (the varietal native to India), but Darjeeling tea comes from Camellia sinensis var sinensis (the varietal native to China). Combining the terroir of West Bengal with the flavor of the Chinese tea plant produces the tea we’ve all come to know and love.
And, finally, we get to dark tea
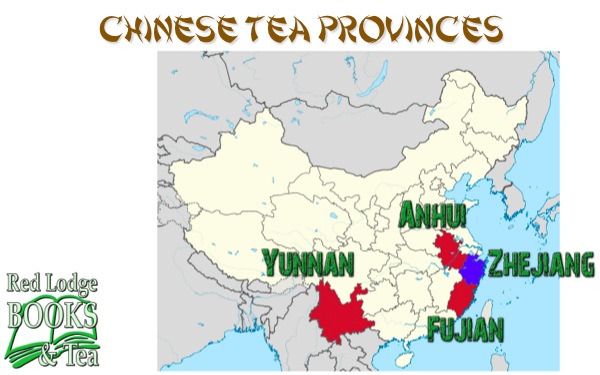
Another geographically-named tea style is pu-erh (also spelled pu’er or puer), named for the town in the Yunnan province of China where the style originated. Only recently has the tea industry really started using the more generic name of “dark tea” to refer to fermented (as opposed to oxidized) teas.
There are two ways to make pu-erh: sheng and shu (also spelled shou).
SHENG (a.k.a. raw or green pu-erh) is the more prized by collectors. The tea is stored in a slightly damp humidity-controlled environment and allowed to slowly ferment. It’s generally not considered ready to drink for years after being picked. Shengs have the same vegetal flavors and aromas as a good Chinese green tea, but with very complex earthy undertones.
SHU (a.k.a. ripe or cooked or black pu-erh) gets a bacterial “kick-start” to the fermentation process, so it’s ready to drink within a matter of months instead of years. Shu pu-erh requires very little steeping time (I’ve spoken to producers that recommend as little as ten seconds), and many pu-erh drinkers start with a “wash,” where you add boiling water, swirl for a few seconds, and pour it off before doing a “real” steeping. Shu pu-er tends to be extremely earthy, with a “composty” undertone. The flavor profile is even richer and deeper than a strong black tea (often reminiscent of a good Keemun), but with very little astringency.
There are several common shapes of pu-erh cakes, including rectangular bricks, bird-nest shapes (“tuo cha”), and flat disks (“beeng cha”).

The standard size for a beeng cha (like the one pictured above, which I wrote more about) is 357 grams, although they can be found in smaller sizes as well. I’ve found several suppliers for 100g beeng chas lately, which is a more affordable alternative for someone new to dark teas or someone sampling a new variety.
Tuo chas, on the other hand, are available in a wide variety of sizes usually centered around 80-120g. Mini tuo chas have become quite common. Each is a single serving of tea, roughly 5g.
Bricks can be found in a variety of sizes as well.
Something new (to me, anyway) is the log-shaped dark tea. My wife, Kathy, and I found these at the World Tea Expo (the big annual industry trade show for tea people) a couple of weeks ago. The ones we purchased for our tea bar are logs about 3.625 kilos (8 pounds), 25 inches long by 5 inches in diameter. We’re selling a single log in its bamboo wrapping with a canvas carry tote for $99.99, but most people will be more interested in slices taken from the log.
In the picture below, Kathy and I are posing with what the tea grower calls the world’s largest log of dark tea. If it puts the size of that tea log in perspective, I am 6’5″ tall (195 cm) not counting the hat and boots. Not having a spare thousand dollars laying around, we didn’t buy that one!
Fun Blends: Terracotta Army Chocolate Pu–erh
My wife, Kathy, is a chocoholic who loves tea. She has tried chocolate tea blends from various companies, and decided that she’s not a fan of chocolate tea blends using mild-flavored tea. She likes to be able to taste the chocolate and the tea.
Gwen and Kathy and I experimented and came up with a blend based on a loose-leaf shu (ripe) pu-erh blended with cocoa nibs and vanilla. It was a struggle getting the balance just right, but the result was so good, we decided to give it a permanent home on the tea bar’s menu. After struggling for a while to come up with a name reflecting its Chinese origins: Terracotta Army Chocolate Pu-erh.
The Logo
I love having fun with tea logos. As I’ve mentioned before (see list below), a series of local artists have been creating logos for our house blends. This one was produced by artist (and art history professor) Kory Rountree:
We love that Kory started with one of the soldiers in the real Terracotta Army, made him chocolate, and gave him a cup of tea. He actually provided two logos for us to choose between. We picked the one above because it is clear, simple, and easy to identify even at small sizes. I actually prefer the alternative (shown below), but it’s just too complex to put on a little tea label.

The details are what really make this one. Note the eyes on the soldier above and left of the chocolate soldier. You can almost hear him thinking “Yummy!” The one above and to the right has a similar, but more subtle expression. It’s not obvious at first glance, but if you look closely, the soldier to the right of the chocolate fellow is holding a piece of the melted/broken chocolate arm in one hand, and a cup of chocolate pu-erh tea in the other.
Thank you, Kory! Another awesome logo for the collection!
This is the latest in a collection of labels I’ve written about here before:
Far Too Good For Ordinary People
 Part of the fun of the tea business is the names. The names of the teas themselves are wonderful — from classics like Iron Goddess of Mercy to house blends like Mr. Excellent’s Post-Apocalyptic Earl Grey — but the industry terminology is fun as well. Let’s take the “orange pekoe” grading system used for black teas from Sri Lanka (Ceylon) and India.
Part of the fun of the tea business is the names. The names of the teas themselves are wonderful — from classics like Iron Goddess of Mercy to house blends like Mr. Excellent’s Post-Apocalyptic Earl Grey — but the industry terminology is fun as well. Let’s take the “orange pekoe” grading system used for black teas from Sri Lanka (Ceylon) and India.
I can’t count the number of times someone has come into the tea bar telling me they like flavored teas. “You know, something like that Orange Pekoe stuff.”
“Actually,” I have to explain, “that’s not a style of tea, but a grade. And it has no flavorings at all. Nope. No orange in it.”
What I generally don’t go on to explain is how that whole pekoe grading system works. Let’s start with the words “orange” and “pekoe.” A pekoe is a tea bud, the unopened leaf at the very tip of a branch. A pekoe tea, then, would contain the buds and smallest leaves adjacent to the buds. To further confuse matters, the word “pekoe” in grading tea doesn’t mean quite the same thing as it means when speaking of tea buds. We’ll get to that in a moment.
“Orange,” as I mentioned above, has nothing to do with fruit. What it does actually mean is open to debate. It could refer to the color of the oxidized leaves. It could refer to the color of the brewed tea. It could refer to the Dutch royal family (the House of Orange). All that really matters is that in tea grading, any whole-leaf black tea qualifies as an Orange Pekoe.
So what about all those other letters? The joke in the tea business is that FTGFOP stands for “Far Too Good For Ordinary People.” In reality, it stands for “Fine (or Finest) Tippy Golden Flowery Orange Pekoe.” Referring to a grade of tea as the “finest” isn’t good enough, of course, so there are actually several grades above that. Here are the basic grades:
- OP (Orange Pekoe): A whole-leaf black tea.
- FOP (Flowery Orange Pekoe): Long leaves with some tips (pekoes).
- GFOP (Golden Flowery Orange Pekoe): An FOP with more tips.
- TGFOP (Tippy Golden Flowery Orange Pekoe): A GFOP with a whole lot of tips.
- FTGFOP (Finest Tippy Golden Flowery Orange Pekoe): Traditionally the highest-quality grade of black tea.
- SFTGFOP (Special Finest Tippy Golden Flowery Orange Pekoe): Sorry, we needed one more grade.
For the true connoisseur, a grading system can never have fine enough gradations, so you can also elevate each of these grades another half-point by adding the number “1” after it. Thus, despite the industry joke, there are three grades of tea better than FTGFOP (FTGFOP-1, SFTGFOP, and SFTGFOP-1).
Let me reinforce an important point here: this grading system is used only for black teas, and only in a few countries. China, for example, rarely grades its teas using this system, although Kenya is doing more of it as their teas increase in quality.
Are there lower grades?
I thought you’d never ask.
The majority of tea consumed in the U.S. and U.K. is in teabags. In a traditional teabag, there’s little room for the hot water to circulate or the leaves to expand as they absorb water. The solution? Break those leaves into smaller pieces. That exposes more of the surface area of the leaf to water and allows more tea (by weight) to fit into a smaller area.
OP-grade teas use whole leaves. There is a series of grades below OP that include the letter B for “Broken.” BOP (Broken Orange Pekoe), FBOP, GBOP, and so on. There are also a couple of broken grades below BOP, including BP (Broken Pekoe) and BT (Broken Tea).
So that’s what’s used in teabags? Nope. Let’s drop another grade.
After the processing facility has sorted out all of the Pekoe and Broken Pekoe grades, what’s left is known as “fannings.” Grades like PF (Pekoe Fannings), FOF (Flowery Orange Fannings), and TGFOF (Tippy Golden Flowery Orange Fannings). These are the grades used in most decent-quality teabags (high-end teabags may use whole-leaf teas, typically in a sachet-style bag).
“Decent-quality teabags?” I hear you cry. “Are you implying there’s another grade below fannings?”
Yes. Yes I am.
The smallest-sized particles of tea — too small to be fannings — are called “dust.” There are different grades of dust, of course, depending on the tea leaves they come from. You may encounter PD (Pekoe Dust), GD (Golden Dust), FD (Fine Dust), and others. Typically, though, grades like that don’t make it onto commercial packaging.
So these lower grades suck?
No, I didn’t say that.
Fannings from an extraordinary tea will produce a much better drink than whole leaves from a mediocre tea. There are a lot of factors to take into consideration, but the number one factor is your own preferences. As I’ve said before on this blog, I’m not a tea Nazi. It won’t hurt my feelings a bit if you prefer the cheapest grade of Lipton teabags to my shop’s whole-leaf FTGFOP-1 First Flush Darjeeling. In fact, it would be quite a waste of money to buy a tea you don’t like.
In a way, buying tea that’s highly-graded on the pekoe system is like buying organic. What it really tells you is that you’re dealing with a legitimate tea producer that cares enough about their product to pick it right and have it graded by experts.
What’s the difference between Japanese and Chinese green tea?
As I did last month and the month before, I took a look at some of the search terms that brought people to this blog and found a question that I didn’t really address. This time: “What’s the difference between Japanese and Chinese green tea?” The obvious smart-aleck answer is that one comes from Japan and the other comes from China, but it runs a bit deeper than that.
First off, it’s not the plants themselves. The first varietal discovered of the tea plant is Camellia sinensis var. sinensis: the Chinese tea plant. About 1400 years ago, during the Sui Dynasty, Buddhist monks introduced tea — and the tea plant — to Japan. This means that the same varietal of tea plant is growing in China and Japan.
Terroir, on the other hand, can definitely have an effect. The climate, soil, and other factors can definitely affect the taste of the tea. Also, the Japanese have been crossbreeding and developing their strains of tea plant for over a millennium.
The biggest factor in the taste, though, is a very simple one: the process.
The difference between black tea and green tea is oxidation. Black tea is fully (or near-fully) oxidized, while green tea is not oxidized at all. There is an enzyme in the tea leaf that starts the oxidation process as soon as the leaf has been broken or bruised. Making green tea requires a “kill green” step that destroys the enzyme and stops the tea from oxidizing. That step requires heating the tea leaves quickly to at least 140 degrees.
To make Japanese green teas, such as sencha, bancha, and gyokuro, the leaves are steamed. To make Chinese green teas, such as dragonwell or gunpowder tea, the leaves are pan-fired. Just this simple difference in processing gives Japanese teas a rich grassy flavor and Chinese greens more of a vegetal character.
Granted, I am oversimplifying, but this is the fundamental answer to the question.
A Nice Cup of Tea
On January 12, 1946, the Evening Standard published an essay by George Orwell entitled “A Nice Cup of Tea.” Like almost everyone else in my generation, I had to read his books Nineteen Eighty-Four and Animal Farm in school. They told us a lot about society and a lot about English culture, but not much about tea.
Orwell was British, and born in 1903. These two facts tell you a lot about how he viewed tea. I’ve written before about “Tea Nazis,” who believe that their way of preparing tea is the only way to prepare tea, and this essay is a marvelous example of that philosophy in action.
He opens the essay by saying that if you look up “tea” in a cookbook it’s likely to be unmentioned. That was very true in 1946. It is less true now, but even though there are a lot of wonderful books about tea, mainstream cookbooks generally find it unnecessary to describe how to prepare a pot (or a cup) of tea.
Orwell continues by pointing out that tea is a mainstay of civilization in England, yet the “best manner of making it is a subject of violent disputes.” Judging from conversations I’ve had with British friends, I’d have to agree with that. His next paragraph sets the tone for everything that follows:
“When I look through my own recipe for the perfect cup of tea, I find no fewer than eleven outstanding points. On perhaps two of them there would be pretty general agreement, but at least four others are acutely controversial. Here are my own eleven rules, every one of which I regard as golden:”
Since in my humble opinion just about everything related to preparing tea is subjective, I’d like to present my own take on Orwell’s eleven rules. Lets look at them one at a time.
“First of all, one should use Indian or Ceylonese tea. China tea has virtues which are not to be despised nowadays — it is economical, and one can drink it without milk — but there is not much stimulation in it. One does not feel wiser, braver or more optimistic after drinking it. Anyone who has used that comforting phrase ‘a nice cup of tea’ invariably means Indian tea.”
Here, I must vehemently disagree with Mr. Orwell. Perhaps the fact that he was born in India is showing through here. There is excellent tea from China (and Japan and Kenya and Taiwan…). If you want a beverage that will make you feel “wiser, braver or more optimistic,” I would recommend tequila. If you want tea that tastes good, you can find it all over the world.
Incidentally, when Orwell refers to “Ceylonese” tea, he means tea from the country that was called Ceylon when he wrote this essay, but became Sri Lanka when it achieved independence in 1948. We still typically call tea from Sri Lanka “Ceylon” tea.
“Secondly, tea should be made in small quantities — that is, in a teapot. Tea out of an urn is always tasteless, while army tea, made in a cauldron, tastes of grease and whitewash. The teapot should be made of china or earthenware. Silver or Britannia-ware teapots produce inferior tea and enamel pots are worse; though curiously enough a pewter teapot (a rarity nowadays) is not so bad.”
He has an excellent point about the small quantities. To me, this means preparing it by the cup rather than by the pot, and there is a lot of excellent teaware available for that purpose. Although china, earthenware, and ceramic teapots do add something to the tea, using plastic or glass pots allows you to watch the tea steep. It also adds (and detracts) nothing to the flavor.
“Thirdly, the pot should be warmed beforehand. This is better done by placing it on the hob than by the usual method of swilling it out with hot water.”
I agree that pre-warming the pot helps to keep the water hot as the tea steeps.
“Fourthly, the tea should be strong. For a pot holding a quart, if you are going to fill it nearly to the brim, six heaped teaspoons would be about right. In a time of rationing, this is not an idea that can be realised on every day of the week, but I maintain that one strong cup of tea is better than twenty weak ones. All true tea-lovers not only like their tea strong, but like it a little stronger with each year that passes — a fact which is recognized in the extra ration issued to old-age pensioners.”
My biggest problem with this “rule” is the statement that “all true tea-lovers not only like their tea strong.” In fact, many tea lovers like a shorter steeping time so that the flavor of the tea isn’t overwhelmed by the bitterness and tannins that come out later in the steep.
“Fifthly, the tea should be put straight into the pot. No strainers, muslin bags or other devices to imprison the tea. In some countries teapots are fitted with little dangling baskets under the spout to catch the stray leaves, which are supposed to be harmful. Actually one can swallow tea-leaves in considerable quantities without ill effect, and if the tea is not loose in the pot it never infuses properly.”
Philosophically, he’s right. Allowing the water to circulate freely through the leaves does improve the infusion process. I do prefer not to consume the leaves (unless I’m drinking matcha), but a proper modern infuser will catch pretty much all of them.
“Sixthly, one should take the teapot to the kettle and not the other way about. The water should be actually boiling at the moment of impact, which means that one should keep it on the flame while one pours. Some people add that one should only use water that has been freshly brought to the boil, but I have never noticed that it makes any difference.”
Clearly, Mr. Orwell was aware of only one kind of tea: black. While boiling water is the right way to go for black and pu-erh tea, you get much better results with green and white tea if you use cooler water. I won’t get into the oolong debate at the moment…
The little aside that he snuck in here about freshly-boiled water is perhaps the biggest point of argument I hear from tea lovers. Does your tea really taste different if the water is heated in a microwave instead of being boiled in a teapot? Does the tea taste different if you reboil water that has been boiled before? In a blind taste test, I can’t tell the difference. Perhaps you can.
“Seventhly, after making the tea, one should stir it, or better, give the pot a good shake, afterwards allowing the leaves to settle.”
I confess. I do this.
“Eighthly, one should drink out of a good breakfast cup — that is, the cylindrical type of cup, not the flat, shallow type. The breakfast cup holds more, and with the other kind one’s tea is always half cold — before one has well started on it.”
Your cup is as personal as your clothing or your car. Most of the time, I use a 16-ounce ceramic mug made by a local potter. When I’m trying a new tea, I make the first cup in a glass mug so I can see it better. I typically use a smaller cup for matcha, a bigger one for chai lattes, and a bigger one than that for iced tea.
“Ninthly, one should pour the cream off the milk before using it for tea. Milk that is too creamy always gives tea a sickly taste.”
Unless I’m drinking chai, I do not add milk to my tea. I have made the occasional exception (I actually like milk in purple tea), but I generally prefer to taste the tea, not the milk.
“Tenthly, one should pour tea into the cup first. This is one of the most controversial points of all; indeed in every family in Britain there are probably two schools of thought on the subject.
The milk-first school can bring forward some fairly strong arguments, but I maintain that my own argument is unanswerable. This is that, by putting the tea in first and stirring as one pours, one can exactly regulate the amount of milk whereas one is liable to put in too much milk if one does it the other way round.”
When I make chai, I don’t use either of Orwell’s methods. I find that the spices extract better with the lipids in the milk present than they do in water alone. In other words, I heat the milk and add it to the water while the tea is steeping. It changes the flavor considerably.
When I’m adding milk to any other tea, I typically put it in the cup first and then add tea to it.
“Lastly, tea — unless one is drinking it in the Russian style — should be drunk without sugar. I know very well that I am in a minority here. But still, how can you call yourself a true tea-lover if you destroy the flavour of your tea by putting sugar in it? It would be equally reasonable to put in pepper or salt.”
Good point, Mr. Orwell. Now please substitute the word “milk” for “sugar” in this paragraph. Then go back and read rule nine. I don’t sweeten my tea (chai being the exception again — I like some honey in it), but I see nothing wrong with doing so. Adding a bit of sugar is no different than adding a bit of milk.
Oh, and by the way, tea was traditionally prepared in salt water in ancient China. And one of my favorite chai blends does, indeed, contain pepper.
Orwell continues…
“Tea is meant to be bitter, just as beer is meant to be bitter. If you sweeten it, you are no longer tasting the tea, you are merely tasting the sugar; you could make a very similar drink by dissolving sugar in plain hot water.
Some people would answer that they don’t like tea in itself, that they only drink it in order to be warmed and stimulated, and they need sugar to take the taste away. To those misguided people I would say: Try drinking tea without sugar for, say, a fortnight and it is very unlikely that you will ever want to ruin your tea by sweetening it again.”
Again, Orwell is speaking only of black tea here. I do not expect bitterness in, for example, a Long Jing Dragonwell green tea. And I would argue that there are a lot of fine black teas that have minimal bitterness: Royal Golden Safari from Kenya, to pick a favorite of mine.
If I had to pick one issue to argue in this essay, it would be that George Orwell considers all tea to be the same (after eliminating the majority of the world’s production by limiting himself to India and Sri Lanka). Even within the world of black tea, there is immense diversity. I don’t use the same preparation methods or expect the same results for a malty Assam tea and a delicate first flush Darjeeling — much less a smoky Chinese lapsang souchong.
My recommendation? Experiment. Try new teas, and try them first without adding milk or sweetener. Use your supplier’s recommended water temperature and steeping time. Taste the tea. THEN decide whether you want to steep it for a shorter or longer time; whether it needs a bit of milk; whether you’d prefer to sweeten it.
The best tea is your favorite tea, prepared just the way you like it.













 Legend says that tea originated in China in 2737 B.C., over 100 years before the first Egyptian pyramid was built. In this first stop on our
Legend says that tea originated in China in 2737 B.C., over 100 years before the first Egyptian pyramid was built. In this first stop on our