Category Archives: World Tea Tour
Argentina and Yerba Maté: Stop 8 on the World Tea Tasting Tour
While Europe was getting hooked on coffee and Asia was drinking tea, the people of Argentina and Paraguay were enjoying their own indigenous source of caffeine: yerba maté.

Yerba maté comes from a plant called Ilex paraguariensis, a species of holly which contains caffeine and other xanthines. Maté is a traditional beverage throughout South America, typically served hot (well, “warm” by American standards) and shared among friends from a gourd and bombilla (metal or cane straw).
The matés we tasted were:
- Traditional green yerba maté (organic)
- Roasted yerba maté
- Montana huckleberry maté
- Carnival maté
- Eye of the Storm (our house blend minty maté)
Although when it comes to caffeinated drinks, Argentina is mostly known for its yerba maté, the country is the world’s 9th largest producer of tea, with an annual production of about 60,000 tons. Most of that tea is used in blends and iced teas, and it’s pretty rare to find an Argentinian tea on the menu at a tea bar.
In land area, Argentina is the world’s 8th largest country, covering over a million square miles. Their population is just over 40 million, and the main language is Spanish.
Yerba Maté
The word maté actually means “gourd,” a reference to the vessel traditionally used when drinking yerba maté in most of South America. In Paraguay, on the other hand, they often drink their maté cold (they call it tereré) from a guampa, a drinking vessel made from an ox horn.
The total world production of yerba maté is about 500,000 tons, of which about 290,000 tons comes from Argentina: almost five times their annual tea production. The rest is almost all grown in Brazil and Paraguay. This makes it about a $1.4 billion market (in U.S. dollars) — much bigger than the rooibos market we talked about last week. The majority of the maté is consumed in South America, with the largest outside buyer being Syria.
Maté is usually produced like a green tea, with minimal oxidation. The gourd is packed about half full with leaves in an elaborate ritual, and then filled the rest of the way with water at about 150 degrees F. Argentinian children enjoy maté, too, usually prepared with milk.
In the U.S., maté is more often prepared like tea, by steeping in hot or boiling water. A bit of sugar can help to cut the bitterness caused by the hotter water.
We tasted both a plain maté and one of our house blends with peppermint and spearmint added (that one is yummy iced!).
Roasted Maté
It is becoming increasingly popular to roast the maté, producing a drink that is darker and richer. The taste of roasted maté is often compared to coffee or chicory. We tasted a plain roasted maté plus two flavored ones: a “carnival” maté with caramel and Spanish safflower, and a Montana huckleberry maté.
Caffeine and Maté
It was long thought that maté contained a chemical called mateine, similar to caffeine and a member of the xanthine family. Recent research has shown that mateine actually is caffeine, and it just showed up differently in lab tests because of other compounds present in the maté.
Yerba maté contains three different xanthines: caffeine, theobromine, and theophylline. The total caffeine content is higher than a typical cup of tea, but less than a strong coffee. The way the maté is prepared has a great effect on the caffeine content: the temperature of the water, the steep time, and the amount of leaf used all interact to influence how much caffeine is extracted from the leaves into the drink.
When I have some more time, I’ll write a post detailing and illustrating the maté ceremony.
This was the eighth stop on our World Tea Tasting Tour, in which we explore the tea of China, India, Japan, Taiwan, England, South Africa, Kenya, and Argentina. Each class costs $5.00, which includes the tea tasting itself and a $5.00 off coupon that can be used that night for any tea, teaware, or tea-related books that we sell.
For a full schedule of the tea tour, see my introductory post from February.
The Rooibos of South Africa: Stop 7 on the World Tea Tasting Tour
If you’re looking for a drink with all the health benefits of tea, a similarly great taste, but no caffeine, look to South Africa! Rooibos is made from the South African red bush (Aspalathus linearis). Using rooibos instead of tea is a great way to enjoy a caffeine-free hot (or iced) drink without using any chemical decaffeination process. Rooibos is full of antioxidants, Vitamins C and E, iron, zinc, potassium, and calcium. It is naturally sweet without adding sugar.
Rooibos grows only in the Western Cape of South Africa, and a similar plant called honeybush (the Cyclopia plant) grows in the Eastern Cape. Its flowers smell of honey, hence the name. The taste of honeybush is similar to rooibos, though perhaps a bit sweeter. Like rooibos, honeybush is naturally free of caffeine and tannins; perfect for a late-evening drink.
The teas we tasted were:
- Red rooibos (organic)
- Green rooibos (organic)
- Honeybush (organic)
- Jamaica red rooibos (organic, fair trade)
- Bluebeary relaxation (organic, fair trade)
- Iced rooibos
- Cape Town Fog (a vanilla rooibos latte!)
South Africa, as the name implies, sits at the very southern tip of the African continent. It completely surrounds a small country called Lesotho. South Africa covers 471,443 square miles (about three times the size of Montana) and has a population of 51,770,000 (a bit more than Spain). Despite wide open spaces in the middle of the country, the large cities make it overall densely populated.
The country has the largest economy in Africa, yet about 1/4 of the population is unemployed and living on the equivalent of US $1.25 per day.
Red rooibos
Rooibos isn’t a huge part of the South African economy. It does, however, employ about 5,000 people and generates a total annual revenue of around US $70 million, which is nothing to sneeze at. The plant is native to South Africa’s Western Cape, and the country produces about 24,000,000 pounds of rooibos per year.
The name “rooibos” is from the Dutch word “rooibosch” meaning “red bush.” The spelling was altered to “rooibos” when it was adopted into Afrikaans. In the U.S., it’s pronounced many different ways but most often some variant of ROY-boss or ROO-ee-bose.
I’ve written quite a bit about red rooibos in several posts — and about the copyright issues — so I won’t repeat it all here. Rooibos is also great as an ingredient in cooking: see my African Rooibos Hummus recipe for an example.
Green rooibos
Green rooibos isn’t oxidized, so it has a flavor profile closer to a green tea than a black tea. Again, I’ve written a lot about it, so I’ll just link to the old post.
Honeybush
Honeybush isn’t one single species of plant like rooibos. The name applies to a couple of dozen species of plants in the Cyclopia genus, of which four or five are used widely to make herbal teas. Honeybush grows primarily in Africa’s Eastern Cape, and isn’t nearly as well-known as rooibos.
It got its name from its honey-like aroma, but it also has a sweeter flavor than rooibos. It can be steeped a long time without bitterness, but I generally prefer about three minutes of steep time in boiling water.
Jamaica Red Rooibos
I decided to bring out a couple of flavored rooibos blends for the tasting as well. The first is Jamaica Red Rooibos, a Rishi blend. It has an extremely complex melange of flavors and aromas, and is not only a good drink, but fun to cook with as well (see my “Spicing up couscous” post).
Jamaica Red Rooibos is named for the Jamaica flower, a variety of hibiscus. The extensive ingredient list includes rooibos, hibiscus, schizandra berries, lemongrass, rosehips, licorice root, orange peel, passion fruit & mango flavor, essential orange, tangerine & clove oils
BlueBeary Relaxation
BlueBeary Relaxation one of the blends in our Yellowstone Wildlife Sanctuary fundraiser series (the spelling “BlueBeary” comes from the name of one of the bears at the Sanctuary). It’s an intensely blueberry experience that’s become a bedtime favorite of mine. It’s like drinking a blueberry muffin!
Iced rooibos
To make a really good cup of iced rooibos, prepare the hot infusion with about double the leaf you’d use normally, because pouring it over the ice will dilute it. Both green and red rooibos make great iced tea. I prefer both styles unadulterated, but many people drink iced red rooibos with sugar or honey.
Cape Town Fog
This South African take on the “London Fog” is a great caffeine-free latte. To prepare it, you’ll want to preheat the milk almost to boiling. If you have a frother of some kind, use it — aerating the milk improves the taste. Steep the red rooibos good and strong, and add a bit of vanilla syrup or extract. We use an aged vanilla extract for ours. Mix it all up, put a dab of foam on top if you frothed the milk, and optionally top with a light shake of cinnamon.
This was the seventh stop on our World Tea Tasting Tour, in which we explore the tea of China, India, Japan, Taiwan, England, South Africa, Kenya, and Argentina. Each class costs $5.00, which includes the tea tasting itself and a $5.00 off coupon that can be used that night for any tea, teaware, or tea-related books that we sell.
For a full schedule of the tea tour, see my introductory post from February.
The Oolongs of Taiwan: Stop 6 on the World Tea Tasting Tour
Taiwan may not have originated oolong tea, but it is definitely at the forefront of oolongs today. At this stop on the tea tour, attendees learned about what oolong tea actually is, and tasted a variety of Taiwanese oolongs, including Bao Zhong, White Tip Bai Hao, and of course Tieguanyin, better known as “Iron Goddess of Mercy.” We’ll also talk a bit about the history of Formosa tea (Taiwan was called Formosa until the 1940s).
For comparison, we also tasted a couple of Chinese oolongs.
The teas we tasted were:
- Bao Zhong (Pouchong) – Taiwan
- White Tip Bai Hao – Taiwan
- Tieguanyin (Iron Goddess of Mercy) – Taiwan
- Wuyi (Shui Xian) – China
- Qilan (Dark) – China
- Boba (“bubble”) Tea – Taiwan
Officially, Taiwan is known as the Republic of China (ROC). It is an island off the coast of mainland China, which is officially known as the People’s Republic of China (PRC). The PRC lays claim to Taiwan, but the ROC has declared its independence and established its own government, currency, and economy. The island, formerly known as Formosa, is 13,978 square miles — only about a tenth the size of the state of Montana. It’s population, however, is about 23,315,000, which is significantly more than the state of Texas.
A variety of tea styles is produced in Taiwan, but their specialty is oolong. About 20% of the world’s oolong tea comes from this small island.
There have been wild tea plants on Taiwan for a long time. They were first reported to the Western world in a report in 1685. Chinese tea plants were brought out to Taiwan by Ke Chao in the late 18th century, and a Scotsman named John Dodd established a tea export business in 1869. Tea soon became Taiwan’s major export, and the Tea Research Institute of Taiwan was formed in 1926.
Oolong, which means “black dragon” in Chinese, is the most complex of tea styles to produce. Oolongs are generally not crushed or torn, and are only partially oxidized (not fermented), unlike green tea, which isn’t oxidized at all, and black tea, which is fully or almost-fully oxidized.
Generally, we tailor the steep time and water temperature to each individual tea in our tastings, but tonight we wanted to give everyone a solid basis for comparison, so we prepared all of the oolongs in 195-200 degree (F) water and steeped them for two minutes.
Pouchong
Pouchong is often spelled as “Bao Zhong” to more accurately reflect the way it is pronounced. It’s a very lightly oxidized oolong tea that appeals well to green tea lovers. Because of its mild taste and aroma, many flavored oolongs use pouchong as their base.
White Tip Bai Hao
Here’s a tea with many names, including Bai Hao in the east and Oriental Beauty in the west. In the beginning, it was known as “bragger’s tea” because of the origin story (one of the stories that will appear in my new book, by the way), where a farmer went ahead and used leaves that had been chewed up by insects and discovered that the flavor was so wonderfully enhanced that he got twice his normal price at market.
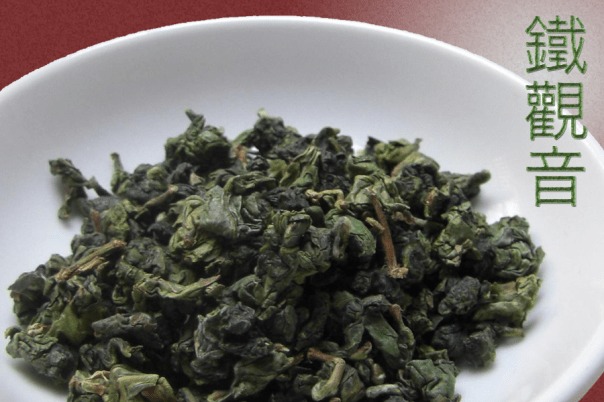
Tieguanyin (Iron Goddess of Mercy)
This style originated in China, but has become a staple of Taiwanese oolong as well. I’ve written about it before. Even with 120 different teas to choose from in my tea bar, it’s rare for me to go more than a couple of days without drinking a few cups of Tieguanyin. It’s generally good for at least 5-7 infusions, and it’s a great everyday tea.
Wuyi Oolong
We then moved to the birthplace of oolong tea: the Wuyi mountains in the Fujian province of China. This tea is highly oxidized and then roasted to give a very full-flavored cup. We tasted it on the first stop (China) of our World Tea Tasting Tour, making this the first tea that’s been in two different tastings.
Qilan Oolong
Staying in that same area, we moved on to an even more oxidized and roasted dark oolong. Qilan (“profound orchid”) is actually a darker and more flavorful tea than many of my favorite black teas, like Golden Yunnan, Royal Golden Safari, and first-flush Darjeeling (all described in previous tasting notes).
Boba Tea
The most recent export from Taiwan is an iced drink they call “boba milk tea,” usually served as “bubble tea” in the United States. It has taken many urban areas here by storm, especially in the Pacific Northwest. Unfortunately, the way most of the mainstream purveyors prepare it, there’s no tea in bubble tea — they use snowcone syrups or similar super-sweet flavorings.
We prepare ours by steeping a strong cup of tea (tonight’s tasting used a mango-flavored tieguanyin as the base). In a cocktail shaker we add ice, simple syrup (sugar water), and a bit of milk. After shaking that into a froth, we pour it over fresh-made tapioca pearls.
This was the sixth stop on our World Tea Tasting Tour, in which we explore the tea of China, India, Japan, Taiwan, England, South Africa, Kenya, and Argentina. Each class costs $5.00, which includes the tea tasting itself and a $5.00 off coupon that can be used that night for any tea, teaware, or tea-related books that we sell.
For a full schedule of the tea tour, see my introductory post from February.
Oolong-related articles on Tea With Gary
-
The Oolongs of Taiwan: Stop 6 on the World Tea Tasting Tour
Taiwan may not have originated oolong tea, but it is definitely at the forefront of oolongs today. At this stop on the tea tour, attendees learned about what oolong tea actually is, and tasted a variety of Taiwanese oolongs, including Bao Zhong, White Tip Bai Hao, and of course Tieguanyin,…
Deepest Africa – The Tea of Kenya: Stop 5 on the World Tea Tasting Tour
When you think of tea, Africa probably isn’t the first place to pop into your mind, but Kenya is the largest exporter of tea in the world. Tea has revitalized their economy, and tea lovers everywhere became winners. Red Lodge Books & Tea works with family owned plantations in Kenya, and was the first tea bar in the United States to serve Kenya’s unique purple tea.

Kenya is known for its black tea, but with their expanding tea economy, the country has expanded into other styles. We tasted some green and white tea from Kenya, along with traditional estate-grown Kenyan black teas and with some fun and different tea you just can’t get anywhere else.
The teas we tasted were:
- White Whisper
- Rift Valley Green Tea
- Golden Safari (black)
- Lelsa Estate FBOP (black)
- Royal Tajiri (black)
- Purple Tea
A quick bit of background on Kenyan tea before we go any farther. As I mentioned earlier, Kenya is the largest exporter of tea in the world, and the third largest producer (after China and India). Largely because of the population difference, Kenya doesn’t consume as much of its product as China and India do. Kenya produces about 345,000 tons of tea per year, but consumes only about 32,000 tons of that. About 9.6% of the world’s total tea production comes from Kenya.
Those are fascinating statistics, but let’s put some human faces on them. When I wrote my first blog post about purple tea in 2011, I was contacted shortly afterwards by a Kenyan woman by the name of Joy W’Njuguna. I had the pleasure of meeting her in 2012 at the World Tea Expo, as you can see in the picture below. She’s not actually that short — it’s just that I’m six-foot-five and I’m wearing a cowboy hat, so she does look like a tiny little thing.
CAUTION: Before doing business with Royal Tea of Kenya or Joy W’Njuguna, please read my post from May 2014. There are at least a dozen companies (mine included) that report paying for tea and never receiving it!
I’ve learned a lot from Joy about Kenya and its tea industry. One telling tidbit is that about half of Kenya’s tea is produced by corporate farms, and the other half by independent growers. I have a soft spot in my heart for the independents, since I own a (very) independent bookstore and tea bar. Joy, in addition to representing her own family business, is involved in a collaborative export business that represents a coalition of independent family farms in Kenya. The big producers there are focused on producing very high volumes of CTC (Crush, Tear, and Curl) tea that ends up in grocery store teabags. The independent growers are focused instead on producing high-quality handmade tea that will catch the attention of the rest of the world.
I like being able to put a face to the products I buy. I like being able to show my customers a picture and say, “See these people? These people hand-picked the tea you’re drinking. Not machines. We know where the tea came from and we know what we’re buying.”
Well, that’s probably enough of a soapbox for the day — or maybe even the month. Let’s move on to the teas that we tasted. If you’re like most of my customers, you didn’t even know Kenya produced a white tea. Heck, until about a year and a half ago, I didn’t know either. So let’s start there:
White Whisper
Silver Needle is one of the flagship teas of China. White Whisper is not a clone, but a Kenyan tea made with the same process. The vast differences in terroir make show from the first sniff. It’s richer and earthier than Silver Needle. Even at the 5:00 steep time we used, it’s less delicate. Personally, though, I love the complexity of this tea. Just pay close attention to that water temperature. You pour boiling water over these leaves and you’re going to ruin it.
Rift Valley Green Tea
The first time I tried this green tea, I wasn’t really impressed. Since it’s a pan-fired tea, I followed the general guidelines for Chinese greens and steeped it for three minutes. Next pass, I read the tasting notes from Royal Tea of Kenya, which recommend a thirty-second steep. Really? Thirty seconds? Yep. That’s all this tea needs.
I love the fact that this tea comes from the slopes of Mount Kenya. Some of my best memories of my trip to Kenya when I was in high school center around that area and the day and night we spent at the Mount Kenya Safari Club. What a wonderful place!
Royal Golden Safari
I’ve written about this tea before. It’s one of my favorite black teas. In this session, as in most of my tastings, I got raised eyebrows from people when I poured this and told them it was a black tea. It brews up pale red with just a touch of astringency and appeals to many oolong drinkers. Unlike most black teas, I regularly get four or five infusions out of Golden Safari.
Lelsa Estate FBOP
Next, we moved on to a much more traditional Kenyan black. This FBOP is one of the ingredients I use in Gary’s Kilty Pleasure (my Scottish breakfast blend). The estate in Kericho participates in the Ethical Tea Partnership program, which I appreciate, and the tea has a deep red color and characteristic Kenyan “jammy” notes. The maltiness blends well with Assam tea, and those who take their tea English-style will appreciate how well it takes milk.
Royal Tajiri
“Tajiri” is the Swahili word for “rich,” and this tea lives up to its name. The finely broken leaves mean an intense extraction. If you’re a black tea lover, this one will give you everything you’re looking for — assertive astringency, deep red (almost black) color, and a very complex flavor profile.
Royal Purple Tea
I’ve written so much about purple tea on this blog (here, here, and here) that I’ll skip the background data — although the picture on that slide is new: the tea on the left is a traditional Camellia sinensis, and the one on the right is the purple tea varietal TRFK306/1. The molecular structure in the background of the slide is the anthocyanin. I didn’t have my shipment of handcrafted purple tea yet (and the sample didn’t last long!), so we were unable to compare the orthodox to the handcrafted. I will put up separate tasting notes on that when my main shipment arrives.
I will note that we brewed the orthodox purple tea for this tasting with 170 degree (F) water instead of boiling, as I’ve done in the past. The cooler water brought out more of the complex undertones of the tea and backed the astringency down, making it more to my liking. We tasted this side by side with and without milk. If you haven’t had this tea with milk before, add a bit just to see the fascinating lavender color that the tea turns!
Nandi Chai
I confess. I was bummed that we didn’t get our handcrafted purple tea in time for this event. I kind of unloaded on Joy about it, and she was good enough to find me something else fascinating and unique for this event: an African chai. The tea (a blend of purple and traditional black) is from Kenya and the spices are all from Ethiopia.
We closed the tasting with this unique chai, and it went over very well. Instead of taking up half of this post talking about it, I’m going to dedicate a whole blog post to Nandi chai in the near future.
This was the fifth stop on our World Tea Tasting Tour, in which we explore the tea of China, India, Japan, Taiwan, England, South Africa, Kenya, and Argentina. Each class costs $5.00, which includes the tea tasting itself and a $5.00 off coupon that can be used that night for any tea, teaware, or tea-related books that we sell.
For a full schedule of the tea tour, see my introductory post from last month.
Chanoyu: The Way of Tea
This is part two of my article on the Japanese stop of our World Tea Tasting Tour. Part one was posted a few days ago.
The Japanese tea ceremony has been around for a very long time, but it was solidified into its current form in the 1500s by a man named Sen no Rikyū. He was an adherent of a philosophy called wabi-sabi, which honors and treasures simplicity, transience, asymmetry, and finding the beauty in imperfection. Rikyū applied this to the tea ceremony, developing what became known as chanoyu: the Way of Tea.
He removed unnecessary ornamentation from tearooms, typically reducing the decor to a single scroll on the wall and a flower arrangement designed to harmonize with the garden outside. Everything else in the room was functional. Chanoyu teaches four fundamental principles known as wa kei sei jaku, intended to be not only the core of the tea ceremony, but a representation of the principles to incorporate into daily life.
Wa (harmony) was his ultimate ideal. From harmony comes peace. Guest and host should be in harmony and man should strive for harmony with nature, rather than attempting to dominate nature.
Kei (respect) allows people to accept and understand others even when you do not agree with them. In a tea ceremony the guest must respect the host and the host must respect the guest, making them equals. The simplest vase should be treated as well as the most expensive, and the same politeness and purity of heart should be extended to your servant as to your master.
Sei (purity) is a part of the ritual of the tea ceremony, cleaning everything beforehand and wiping each vessel with a special cloth before using it. But that is only an outward reflection of the purity of the heart and soul that brings the harmony and respect. In accordance with wabi-cha, imperfection was to be prized here as well. To Rikyū, the ultimate expression of purity was the garden after he spent hours grooming it and several leaves settled randomly on the assiduously manicured walkway.
Finally, Jaku (tranquility) is the ultimate goal of enlightenment and selflessness. It is also the fresh beginning as you go back with fresh perspective to examine the way you have chosen to implement harmony, respect, and purity into your life.
There is a long list of implements that are used in the preparation of matcha, which is the powdered tea used in the tea ceremony. The four that I concentrated on in this class were the bowl, scoop, whisk, and caddy. It could be argued that others are as important, or even more important, but I chose to focus on the ones that are used at home when you make matcha, even if you are not participating in a tea ceremony. The link in the slide above is a great place to learn all about the ceremony itself, and the site contains a detailed list of chanoyu utensils.
In preparing matcha, the bamboo scoop is used to take tea powder and place it in the bowl. After adding water, the whisk is used not only to mix the powder, but to aerate the mixture, leaving it slightly frothy.
Of all of the tools of chanoyu, the bowl is probably the most personal.
We were lucky enough to have Karin Solberg, who created the matcha bowls we sell at our store, talk about the process of creating and decorating the bowls. Karin has done some lovely work, and we enjoyed learning from her. There is a picture showing some of her bowls in part 1 of this article.
I have said many times before that tea is a very personal thing. Nobody can tell you what tastes good to you. The “right” way for me to enjoy a particular tea could be quite different than the “right” way for you to enjoy that same tea. To Rikyū, however, the tea ceremony was not about what made your matcha taste the best. It was all about using the ritual to clear your mind and help you to see things more clearly. It was about achieving harmony, respect, purity, and tranquility.
Outside of the ceremony, however, I would argue that your way of relaxing is the right way of relaxing, whether it means sitting on your front porch with a steaming hot cup of Earl Grey, preparing a delicate silver needle tea to enjoy with a friend, or laying back in the bathtub with a fragrant jasmine green tea. Tea should be a pleasure, not a chore, and the ceremony is about sharing that pleasure with your friends and guests.
If you live in the area and were unable to attend this session, I sure hope to see you at one of our future stops on our World Tea Tasting Tour. Follow the link for the full schedule, and follow us on Facebook or Twitter for regular updates (the event invitations on Facebook have the most information).
Japan – Bancha to Matcha: Stop 4 on the World Tea Tasting Tour
We’re very excited to be working with resident artist Karin Solberg from the Red Lodge Clay Center, and we are featuring some of her matcha bowls in the store, and she came in to talk about them at this stop in the tour.
The teas we tasted were:
- Organic Sencha
- Gyokuro
- Organic Houjicha (roasted green tea)
- Organic Genmaicha (toasted rice tea)
- Organic Matcha
- Kukicha (“twig tea”)
- Bancha (“coarse sencha”)
- Sencha (“decocted tea”)
- Gyokuro (“jade dew”)
It’s Always Tea Time in India: Stop 3 on the World Tea Tasting Tour
India: the world’s second-largest producer of tea. Our third stop on the tasting tour explored the world of Indian estate teas, focusing on three large and well-known tea regions in the country: Darjeeling, Assam, and Nilgiri. Red Lodge Books & Tea imports directly from estates in Darjeeling and Assam. We compared single-source estate teas (think single-malt Scotch) from Glenburn, Khongea, and Tiger Hill estates to a blended 2nd-flush Darjeeling using tea from Marybong, Lingia, and Chamong estates.
We also explored the rich history of tea in India, from the British East India Company through the modern independent tea industry, and looked at the rating system used for Indian teas, which I wrote about last month here on “Tea With Gary”
The teas we tasted were:
- 1st Flush Darjeeling FTGFOP-1 — Glenburn Estate
- Organic 2nd Flush Darjeeling — Marybong, Lingia & Chamong Estates
- Autumn Crescendo Darjeeling FTGFOP-1 — Glenburn Estate
- Green Darjeeling — Glenburn Estate
- Assam Leaf — Khongea Estate
- Nilgiri FOP Clonal — Tiger Hill Estate
As I mentioned above, India is the 2nd largest producer of tea in the world, but 70% of their tea is consumed domestically, so they don’t play as big a role in the export market as countries like Kenya.
Darjeeling
Darjeeling is the northernmost district in North Bengal. Of the 1,842,000 people who live there, over 52,000 make their living through tea. Darjeeling tea, often called the Champagne of Teas, is made from Camellia sinensis var. sinensis, the Chinese varietal of the tea plant, unlike tea from most of the rest of India, which is made from their native Camellia sinensis var. assamica.
Despite the generalization that black tea is always 100% oxidized (often incorrectly called “fermented”), most Darjeeling black teas are, like oolongs, not completely oxidized. While Darjeeling is known mostly for its black tea, there are oolongs and green teas produced there.
To be called “Darjeeling,” the tea must be produced at one of the 87 tea gardens (estates) in the Darjeeling district. Alas, the majority of tea sold with that name is not actually Darjeeling. Each year, the district produces about 10,000 tonnes of tea, and 40,000 tonnes show up for sale on the global market. In other words, 3/4 of the “Darjeeling” tea in the stores isn’t Darjeeling! That’s why we choose reputable suppliers at our store, buying most of it directly from the estate.
Darjeeling tea changes dramatically by the picking season, which is why we chose three different black Darjeelings for this tasting.
1st Flush Darjeeling FTGFOP-1
The first tea we tasted was a first-flush Darjeeling from the Glenburn Estate, where we get most of our Darjeeling teas. Glenburn was started by a Scottish tea company in 1859, but has now been in the Prakash family for four generations. The estate is 1,875 acres (with 700 under tea), and produces 275,000 pounds of tea per year. They are located at 3,200 feet altitude and get 64-79 inches of rain per year. Glenburn employs 893 permanent workers, plus temporary workers during the picking season.
2nd Flush “Muscatel” Darjeeling
Our next tea was an organic 2nd flush blend by Rishi, using Darjeeling teas from Marybong, Lingia & Chamong Estates. It was specifically blended to bring out the characteristic “muscatel” flavor and aroma associated with second-flush Darjeelings.
Autumn Crescendo Darjeeling FTGFOP-1
For the third tea, we went back to Glenburn and selected an autumn-picked tea. Unlike the first two, we steeped this using full boiling water for three minutes, bringing out the undertones one might otherwise miss.
Green Darjeeling
To wrap up the Darjeeling teas, we tasted a green Darjeeling from last fall. It’s an interesting hybrid of Chinese varietal and processing methodology blended with Indian terroir.
Assam
Assam is a state in northeast India with a population of over 31 million and an area of over 30,000 square miles. If Darjeeling is the champagne of tea, then Assam would be the single malt Scotch of tea. Hearty and malty, this lowland-grown tea comes from the assamica varietal of the tea plant.
Assam Leaf Tea
The Assam tea that we tasted is from the Khongea Estate, which has 1,200 acres of land with 1,100 of that under tea. Sitting at 300 feet altitude, the estate gets 150-200 inches of rain per year, making drainage very important. They employ 1,202 permanent workers (again, more during picking), and produce 2,640 pounds of tea per year.
Since Assam tea is frequently used in breakfast blends, we tasted this one with nothing added and then with milk, as most English tea drinkers (and many Indian tea drinkers) prefer.
Nilgiri
Nilgiri is the westernmost district of the state of Tamil Natu. It is smaller (950 square miles) and less populated (735,000 people) than Darjeeling, and quite high elevation, with tea growing between 6,500 and 8,500 feet altitude.
Tiger Hill Nilgiri FOP Clonal
The tea that we chose from Nilgiri comes from the Tiger Hill Estate in the Nilgiris (the “Blue Mountains” for which the district is named). They have 640 acres under cultivation, almost all of which is “clonal,” meaning that it was grafted onto other rootstock from a few mother plants. Tiger Hill has been producing tea since 1971.
This was the third stop on our World Tea Tasting Tour, in which we explore the tea of China, India, Japan, Taiwan, England, South Africa, Kenya, and Argentina. Each class costs $5.00, which includes the tea tasting itself and a $5.00 off coupon that can be used that night for any tea, teaware, or tea-related books that we sell.
For a full schedule of the tea tour, see my introductory post from last month.
Tea. Earl Grey. Hot: Stop 2 on the World Tea Tasting Tour

Update: The story of the origin of Earl Grey tea is one of the chapters in my book, Myths & Legends of Tea. Check it out!
England may not grow many tea plants, but the United Kingdom has had a massive impact on the development and popularization of tea since the 1660s. Our second stop on the Red Lodge Books & Tea World Tea Tasting Tour explored the world of Earl Grey tea, from the Right Honourable Charles Grey (for whom Earl Grey tea is named) to Star Trek TNG’s Captain Jean-Luc Picard. Earl Grey isn’t a single tea, but a broad range of styles. We carry nine different Earl Greys, of which over half are our own house blends, made right here in Red Lodge. The teas we tasted were:
- Organic Ancient Tree Earl Grey
- Lady Greystoke
- Jasmine Earl Green
- Coyotes of the Purple Sage
- Fifty Shades of Earl Grey
- Mr. Excellent’s Post-Apocalyptic Earl Grey
We started out with a discussion of the history of Earl Grey tea. The common myth is that the tea blend was presented to Charles, the 2nd Earl Grey by a Chinese mandarin after Charles (or one of his men) saved the life of the mandarin’s son on a trip to China. In reality, Charles never set foot in China, and the history has a more mundane beginning. The Earl lived at Howick Hall, which had a high lime (calcium) content in its water. This gave his tea an off-flavor and he (or possibly Lady Grey, depending on who’s telling the story) consulted a tea expert for advice. This tea expert — possibly a Chinese mandarin, we don’t know — came up with the idea of adding the oil of the bergamot orange (Citrus bergamia) to the tea. This is what was served in Howick Hall, and the formula was eventually presented to Twinings by the Earl and it became one of their regular offerings. Twinings changed the formula a couple of years ago, but that’s another story. Before we leave the subject of bergamot, by the way, the word is Italian, not French, so the “T” at the end is pronounced. I have heard a lot of tea people talk about “bergamoh,” but it is actually pronounced just the way it is spelled. Tea purists who scoff at Earl Grey often use the word “perfumey” to describe it. There’s a reason for that. By some estimates, as much as half of women’s perfumes contain bergamot oil, and about a third of men’s fragrances. The first Earl Grey that we tasted is Ancient Tree Earl Grey from Rishi — a wonderful blend that does quite well in our tea bar. This amazing tea won “Best Earl Grey Tea” at the 2008 World Tea Championship. Next, we moved on to a house blend called Lady Greystoke. This is my take on lavender/vanilla Earl Grey, a blend which many tea shops would call Lady Grey, despite the trademark violation. Lady Grey tea is named for Mary Elizabeth Grey, the wife of Lord Charles, 2nd Earl Grey. Our Lady Greystoke is named for Jane Porter, who married Tarzan to become Lady Jane Greystoke (the full story is in an earlier blog post). For people that enjoy the bergamot, but want a milder tea, many shops offer an Earl Green or Earl White, and perhaps a caffeine-free Earl Red made from rooibos (yes, we have all three of those). For a different twist, we offered up a Jasmine Earl Green. Lightly perfumed with both with jasmine blossom and bergamot oil, it’s the most delicate of the teas we tasted. Next, we come to a popular blend of ours that really captures the character of the American West: a sage-based Earl Grey we call Coyotes of the Purple Sage. I know, it sounds rather strange, but the flavor mix really works. The literary allusion in this one comes from Zane Grey’s book, Riders of the Purple Sage. Yes, it’s a Zane Grey Earl Grey! For the story of the logo and blend, see my earlier blog post about it. The next tea also has a book theme — you can tell we have a combination tea bar and bookstore — but I’m not going to call this one a “literary” allusion, as nobody would refer to the Fifty Shades of Grey books as “literature.” I came up with the blend just for fun, with lots of punny references to the book, ranging from tea’s color (black and blue) to the rich flavor and overpowering bergamot. It actually ended up being quite tasty, and we’ve been selling quite a bit of it. We wrapped up with a signature house blend that’s completely different — a lapsang souchong-based Earl Grey that we call Mr. Excellent’s Post-Apocalyptic Earl Grey. The full story of that tea has already been told here, so I won’t repeat it. If you live in the area and were unable to attend this session, I sure hope to see you at one of our future stops on our World Tea Tasting Tour. Follow the link for the full schedule, and follow us on Facebook for regular updates (the event invitations on Facebook have the most information). Let us close with a short video explaining the proper way to order a cup of Earl Grey tea:
The World Tea Tasting Tour
Over the next couple of months, I will be taking you on a world tour of tea with a series of tastings and classes focused on teas from all around the world. The events will be at our tea bar on Fridays from 5:00 to 6:30. At each session, we’ll taste five to seven teas from a different country as we explore a bit of the country’s geography and tea culture. I will put a quick summary of each stop on the tour up here on the blog for those who can’t attend or who don’t remember which teas we covered.
The full tour consists of:
Friday, Feb 15 — All the Tea in China
Friday, Mar 1 — Tea. Earl Grey. Hot. (England)
Friday, Mar 8 — It’s Always Tea Time in India
Friday, Mar 15 — Japan: Bancha to Matcha (notes Part 1 and Part 2)
Friday, Mar 22 — Deepest Africa: The Tea of Kenya
Friday, Mar 29 — The Oolongs of Taiwan
Friday, Apr 5 — Rooibos from South Africa
Friday, Apr 12 — Yerba Maté from Argentina
Friday, Apr 26 — China part II: Pu-Erh
Friday, May 3 — India part II: Masala Chai
Each class will cost $5.00, which includes the tea tasting itself and a $5.00 off coupon that can be used that night for any tea, teaware, or tea-related books that we sell.
There will be more information posted on Facebook before each event, including a list of the teas that we will taste in each event.
UPDATE MARCH 9: As I blog about each of these experiences, I’m going to create a link from this post to the post containing the outline and tasting notes. I’ve linked the first two.
UPDATE MARCH 23: I changed the dates of the last two events. There will not be a tasting on April 19.


















































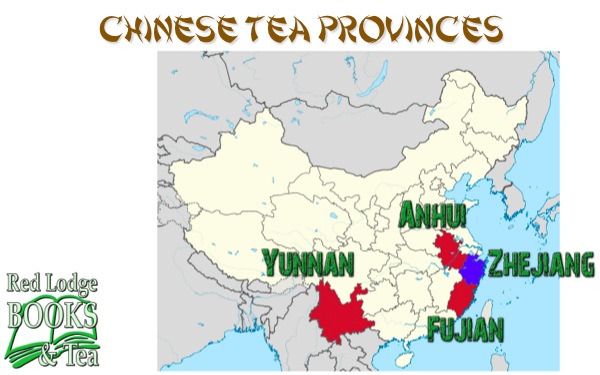
 Legend says that tea originated in China in 2737 B.C., over 100 years before the first Egyptian pyramid was built. In this first stop on our
Legend says that tea originated in China in 2737 B.C., over 100 years before the first Egyptian pyramid was built. In this first stop on our