Blog Archives
Is Your Tea Gluten Free?
The answer to this question should be easy. All tea comes from the Camellia sinensis plant. It is not grain. It contains no gluten.
For those casually following the gluten-free lifestyle, that answer should be enough. But for those with celiac disease, a bit more detail may be required:
A lot of things are called tea that aren’t tea
As the first paragraph said, real tea comes from Camellia sinensis. But many (most?) people refer to anything that involves steeping leaves or flowers in hot water as tea: yerba mate, rooibos, chamomile, honeybush, and so forth. Technically, they are tisanes or infusions, but they are often sold as tea.
So if you’re buying actual black tea, green tea, oolong, pu-erh, or white tea, all is well. If you’re buying “herbal tea,” you’d better take a closer look at that label.
But wait…
Flavored teas have all kinds of additives
You may be getting a nice black tea that’s totally 100% gluten-free, but many flavored blends are sweetened. One of the things they may be sweetened with is malted barley, which does contain gluten. There’s not going to be very much of it, but it may be enough to cause problems for celiac patients.
So if you’re buying unflavored straight black tea, green tea, oolong, pu-erh, or white tea, all is well. If you’re buying flavored teas, you’d better take a closer look at that label.
But wait…
Gluten in teabags? Really?
A number of tea companies use sealants for their teabags that contain gluten. There’s no gluten in the tea itself, but once you dip that bag in boiling water and the glue starts to melt, you’re picking up a tiny bit of gluten. By “tiny bit,” we’re talking a few parts per million in the brewed tea here, which is a tiny fraction of what it takes to cause reactions in someone with celiac disease. But if you’re actually looking for ZERO gluten content, we’re not quite there yet.
So if you’re buying loose-leaf unflavored straight black tea, green tea, oolong, pu-erh, or white tea, all is well. If you’re buying teabags, you’d better take a closer look at that label.
But wait…
Cross-contamination
Now we’re getting into incredibly small amounts, but some tea companies use the same facility for manufacturing tea as they use for manufacturing products that contain gluten. There is a possibility of airborne cross-contamination from those products.
At this point, we might as well be talking about any other food product on the planet. Can we guarantee that there wasn’t a wheat field next to the farm where your tomatoes were grown? A big mug of tea might use 7 grams of tea leaf. Cross-contamination at 1 ppm means 7 micrograms of gluten. That’s about one millionth of the gluten you’d get from a couple of slices of bread or a pint of beer.
According to this article, “research has suggested that a daily gluten intake of less than 10 milligrams (mg) is unlikely to cause significant damage to the intestines in most people with celiac disease.” The gluten you’d pick up from teabag glue or cross-contamination is less than a thousandth of that amount.
That same article says that, “In most parts of the world, regulations say that to be labeled gluten-free, a product can contain up to 20 parts per million (ppm) of gluten.” That means a slice of gluten free bread could still contain 100 times the gluten of a cross-contaminated cup of tea!
I am not a nutritionist, medical practitioner, or scientist, but I think those numbers make it pretty clear that if someone with celiac disease wants to drink a few cups of tea every day, it’s going to be just fine.
As I write this, I’m sipping on a cup of Jinxuan Jade Oolong, a rich buttery semi-oxidized tea that has replaced Iron Goddess of Mercy as my regular morning cup. I steep it 3:00 in boiling water, and then get three more cups out of it, adding a half-minute of steep time to each successive infusion. Although it is of the “milk oolong” style, it contains neither milk nor gluten.
Millennials & Tea

When a new study comes out, it’s interesting to see who spins it how. YouGov released a survey last month comparing American consumption of tea with coffee. Their headline was “Coffee’s millennial problem: tea increasingly popular among young Americans.” Oh, no! A coffee problem!
World Tea News, on the other hand, reported that same survey with the headline, “America’s Youth Embrace Tea.” Oh, boy! Kids are drinking tea.
Most of the articles I read about the survey included this handy-dandy chart:
It pretty clearly indicates that the younger you are, the more likely you are to prefer tea to coffee. The statistic I liked, on the other hand, I turned into the Venn diagram on my header for this article. Of Americans aged 18-29, 18% drink coffee, 27% drink tea, and 39% drink both (the remaining 17% don’t drink either one). In case you’re interested, 998 people were surveyed and 143 of them were in that “millennial” age range of 18-29.
I’m sure there are some people in the tea business that are saying, “This is marvelous! We just have to sit back and wait and we’re going to own this market!” Others are saying, “We really need to get people over 30 to drink more tea.” The coffee industry, of course, has known about this trend for years. That’s why Starbucks bought Tazo and Teavana.
Being a numbers geek, I decided to pull up the PDF of the full report and do a bit of digging. Here are some interesting points you might enjoy:
- The under-30 crowd is much more likely than the older crowd to drink neither coffee nor tea.
- Blacks are over twice as likely to drink tea only (no coffee) than whites or hispanics.
- 64% of Republicans prefer coffee, vs 55% of Democrats and 52% of independents.
- 33% of independents prefer tea, vs 32% of Democrats and 28% of Republicans.
- Middle-income Americans earning $40K-$80K/year are more likely to prefer tea than higher or lower-income Americans.
- 42% of people surveyed are trying to limit their coffee intake vs only 25% that are trying to limit tea.
- Women are much more likely to prefer tea than men
So let’s see here. A tea shop’s target audience is young women? This comes as a surprise to absolutely nobody in the tea business.

I confess that I didn’t expect some of these results. Since Montana is 89% white and 0.4% black, I don’t really have a statistically significant sampling to judge African-American preferences. I do see, however, quite a few Native Americans in the shop getting tea, although I haven’t tried doing any statistical analysis there.
To what do I attribute the tea-drinking millennial trend? The obvious factor is healthier lifestyles, but I would posit something else as well: younger folks are better informed about tea.
I am much more likely to hear an older person say, “I don’t like tea,” because back in their day, tea meant either a teabag full of basic Lipton black tea or the green tea at a Chinese restaurant. Millennials are more likely to have discovered tea in a tea shop that offers dozens — or hundreds — of options. That person who doesn’t like tea may never have tried masala chai, or oolong, or pu-erh, or white tea, or the huge variety of flavored, spiced, and scented options. They’ve probably never experienced the difference between that teabag full of dust and an FTGFOP-1 golden black whole-leaf tea. They may still be under the mistaken impression that latte means coffee, leaving them blissfully unaware of the wealth of tea lattes awaiting them in a good tea shop.
I’ve said many, many times that if you work in the tea business today, your primary job is education. I think this survey shows that tea education is working. Sure, we still sell your basic Earl Grey tea, but younger folks like the ladies in the picture above are well educated about their options. You’re as likely to see them sipping whole-leaf black Vietnamese tea or Indian oolong as you are a peach-flavored white tea or a sage Earl Grey (popular in our corner of Montana).
So let’s get out there and buy Grandma a great cup of tea!
While writing this post, I was drinking Jasmine King Silver Needle tea. It’s a delicate white tea perfectly scented with jasmine blossoms, so that you get the aroma of the jasmine and the flavor of the tea. Yes, jasmine isn’t just for green tea anymore. Hey, that’s a great tagline. Look for it as a blog post title one of these days!
Deepest Africa – The Tea of Kenya: Stop 5 on the World Tea Tasting Tour
When you think of tea, Africa probably isn’t the first place to pop into your mind, but Kenya is the largest exporter of tea in the world. Tea has revitalized their economy, and tea lovers everywhere became winners. Red Lodge Books & Tea works with family owned plantations in Kenya, and was the first tea bar in the United States to serve Kenya’s unique purple tea.

Kenya is known for its black tea, but with their expanding tea economy, the country has expanded into other styles. We tasted some green and white tea from Kenya, along with traditional estate-grown Kenyan black teas and with some fun and different tea you just can’t get anywhere else.
The teas we tasted were:
- White Whisper
- Rift Valley Green Tea
- Golden Safari (black)
- Lelsa Estate FBOP (black)
- Royal Tajiri (black)
- Purple Tea
A quick bit of background on Kenyan tea before we go any farther. As I mentioned earlier, Kenya is the largest exporter of tea in the world, and the third largest producer (after China and India). Largely because of the population difference, Kenya doesn’t consume as much of its product as China and India do. Kenya produces about 345,000 tons of tea per year, but consumes only about 32,000 tons of that. About 9.6% of the world’s total tea production comes from Kenya.
Those are fascinating statistics, but let’s put some human faces on them. When I wrote my first blog post about purple tea in 2011, I was contacted shortly afterwards by a Kenyan woman by the name of Joy W’Njuguna. I had the pleasure of meeting her in 2012 at the World Tea Expo, as you can see in the picture below. She’s not actually that short — it’s just that I’m six-foot-five and I’m wearing a cowboy hat, so she does look like a tiny little thing.
CAUTION: Before doing business with Royal Tea of Kenya or Joy W’Njuguna, please read my post from May 2014. There are at least a dozen companies (mine included) that report paying for tea and never receiving it!
I’ve learned a lot from Joy about Kenya and its tea industry. One telling tidbit is that about half of Kenya’s tea is produced by corporate farms, and the other half by independent growers. I have a soft spot in my heart for the independents, since I own a (very) independent bookstore and tea bar. Joy, in addition to representing her own family business, is involved in a collaborative export business that represents a coalition of independent family farms in Kenya. The big producers there are focused on producing very high volumes of CTC (Crush, Tear, and Curl) tea that ends up in grocery store teabags. The independent growers are focused instead on producing high-quality handmade tea that will catch the attention of the rest of the world.
I like being able to put a face to the products I buy. I like being able to show my customers a picture and say, “See these people? These people hand-picked the tea you’re drinking. Not machines. We know where the tea came from and we know what we’re buying.”
Well, that’s probably enough of a soapbox for the day — or maybe even the month. Let’s move on to the teas that we tasted. If you’re like most of my customers, you didn’t even know Kenya produced a white tea. Heck, until about a year and a half ago, I didn’t know either. So let’s start there:
White Whisper
Silver Needle is one of the flagship teas of China. White Whisper is not a clone, but a Kenyan tea made with the same process. The vast differences in terroir make show from the first sniff. It’s richer and earthier than Silver Needle. Even at the 5:00 steep time we used, it’s less delicate. Personally, though, I love the complexity of this tea. Just pay close attention to that water temperature. You pour boiling water over these leaves and you’re going to ruin it.
Rift Valley Green Tea
The first time I tried this green tea, I wasn’t really impressed. Since it’s a pan-fired tea, I followed the general guidelines for Chinese greens and steeped it for three minutes. Next pass, I read the tasting notes from Royal Tea of Kenya, which recommend a thirty-second steep. Really? Thirty seconds? Yep. That’s all this tea needs.
I love the fact that this tea comes from the slopes of Mount Kenya. Some of my best memories of my trip to Kenya when I was in high school center around that area and the day and night we spent at the Mount Kenya Safari Club. What a wonderful place!
Royal Golden Safari
I’ve written about this tea before. It’s one of my favorite black teas. In this session, as in most of my tastings, I got raised eyebrows from people when I poured this and told them it was a black tea. It brews up pale red with just a touch of astringency and appeals to many oolong drinkers. Unlike most black teas, I regularly get four or five infusions out of Golden Safari.
Lelsa Estate FBOP
Next, we moved on to a much more traditional Kenyan black. This FBOP is one of the ingredients I use in Gary’s Kilty Pleasure (my Scottish breakfast blend). The estate in Kericho participates in the Ethical Tea Partnership program, which I appreciate, and the tea has a deep red color and characteristic Kenyan “jammy” notes. The maltiness blends well with Assam tea, and those who take their tea English-style will appreciate how well it takes milk.
Royal Tajiri
“Tajiri” is the Swahili word for “rich,” and this tea lives up to its name. The finely broken leaves mean an intense extraction. If you’re a black tea lover, this one will give you everything you’re looking for — assertive astringency, deep red (almost black) color, and a very complex flavor profile.
Royal Purple Tea
I’ve written so much about purple tea on this blog (here, here, and here) that I’ll skip the background data — although the picture on that slide is new: the tea on the left is a traditional Camellia sinensis, and the one on the right is the purple tea varietal TRFK306/1. The molecular structure in the background of the slide is the anthocyanin. I didn’t have my shipment of handcrafted purple tea yet (and the sample didn’t last long!), so we were unable to compare the orthodox to the handcrafted. I will put up separate tasting notes on that when my main shipment arrives.
I will note that we brewed the orthodox purple tea for this tasting with 170 degree (F) water instead of boiling, as I’ve done in the past. The cooler water brought out more of the complex undertones of the tea and backed the astringency down, making it more to my liking. We tasted this side by side with and without milk. If you haven’t had this tea with milk before, add a bit just to see the fascinating lavender color that the tea turns!
Nandi Chai
I confess. I was bummed that we didn’t get our handcrafted purple tea in time for this event. I kind of unloaded on Joy about it, and she was good enough to find me something else fascinating and unique for this event: an African chai. The tea (a blend of purple and traditional black) is from Kenya and the spices are all from Ethiopia.
We closed the tasting with this unique chai, and it went over very well. Instead of taking up half of this post talking about it, I’m going to dedicate a whole blog post to Nandi chai in the near future.
This was the fifth stop on our World Tea Tasting Tour, in which we explore the tea of China, India, Japan, Taiwan, England, South Africa, Kenya, and Argentina. Each class costs $5.00, which includes the tea tasting itself and a $5.00 off coupon that can be used that night for any tea, teaware, or tea-related books that we sell.
For a full schedule of the tea tour, see my introductory post from last month.
Kenyan Tea in the News
For some reason, there seems to be a lot going in in the world of Kenyan tea this month!
Kenya is the world’s largest exporter of tea. Not the largest producer, for they consume less than a tenth of the 345,000 tons of tea they produce each year — as opposed to China, which produces about 1.25 million tons, but consumes a staggering 1.06 million tons of it.
The fifth stop on our World Tea Tasting Tour was the Tea of Kenya, which we held last week. I’ll be posting notes from the class and tasting shortly.
One of the things I’m most excited about is a new development in purple tea. The orthodox purple tea that I first wrote about in 2011 has a great story and many benefits. Tastewise, though, it is more astringent than I usually prefer, since I typically don’t take milk in my straight black tea. In other words, it’s just not my cup of tea (I’m allowed to make that pun once a year — it’s in my contract). This year, however, I got a sample of a new handcrafted purple tea from Kenya in February. Ambrosia. Absolutely wonderful stuff. I have a kilo on the way, and I’ll write up some decent tasting notes once it arrives.
For our tea tasting, they sent us a marvelous new chai (An African chai. Who’d have thunk it?) called Nandi Chai, after the Nandi peoples of Kenya. The tea is a blend of Kenyan black and purple varieties, and all of the spices are Ethiopian. I’ll be writing more on that later.
In other news, the Kenyan tea industry is trying to lower its costs and carbon footprint. An article in Tea News Direct says that four factories managed by the Kenya Tea Development Agency (KTDA) are going green through the “Gura project,” which will build a hydroelectric plant on the nearby Gura river. The factories will receive carbon credits from the Clean Development Mechanism, which is part of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
To end on a lighter note, there’s a post on the English Tea Store blog today that included a picture of what they called the ugliest teapot in the world (picture below). I honestly can’t decide whether it’s the ugliest or the most awesome. Had I spotted one when I visited Kenya decades ago, I would have almost certainly purchased it.
Teas, Tisanes, and Terminology
Language evolves. I get that. Sometimes changes make communication easier, clearer, or shorter. Sometimes, however, the evolution of the meaning of a word does exactly the opposite. The subject of this blog is a good example.
The word “tea” refers to the tea plant (Camellia sinensis), the dried leaves of that plant, or the drink that is made by infusing those leaves in water.
The word “tisane” refers to any drink made by infusing leaves in water. Synonyms include “herbal tea” and “herbal infusion.”
Technically speaking, all teas are tisanes, but most tisanes are not teas.
In today’s culture, however, practically anything (except coffee and cocoa) that’s made by putting plant matter in water is called a tea. What’s my problem with that? It makes communication more difficult, less clear, and less terse.
- There is no other single word that means “a drink made with Camellia sinensis.” If we call everything tea, then we have to say “real tea” or “tea from the tea plant” or “Camellia sinensis tea” or something similarly ludicrous every time we want to refer specifically to tea rather than to all tisanes.
- There is a perfectly good word for “leaves infused in water.” There is no need to throw away “tisane” (or “herbal tea” or “infusion”) and replace it with a word that already has another meaning.
“But Gary,” I hear you cry, “people have been calling herbal infusions ‘tea’ for a long time!”
That’s true. I sometimes slip and call rooibos a tea myself. “Herbal infusion” is even an alternate definition of tea in the OED. I still maintain, however, that it makes clear, precise communication more difficult when trying to differentiate between tea (made from the Camellia sinensis plant) and drinks made from chamomile, honeybush, and willow bark.
Rooibos
Other words that go through this process are forced through it. Rooibos, for example, is the name for a specific tisane and the plant it’s made from (Aspalathus linearis). The word is Afrikaans for Red Bush. Despite the longtime use of the term in South Africa (the only place the rooibos plant grows), it was almost unknown in the United States in 1994 when Burke International of Texas registered “rooibos” as a trademark. This meant that in the United States, only Burke and its subsidiaries could use the common name of the plant. Had Burke not surrendered the trademark after starting to lose lawsuits, people would have been forced to come up with a new word.
Unfortunately, that wasn’t a decisive victory, as the South African Rooibos Council is being forced to repeat the process now with a French company.
As more people in the U.S. discover green rooibos, the name “red bush” becomes more confusing anyway. Rooibos, in my humble opinion, should remain the generic term here.
Oxidation vs. fermentation
There are other words in the tea industry that suffer from ambiguity and questionable correctness. You will find quite a bit of tea literature that refers to the oxidation of tea as fermentation. I had a bit of a row with Chris Kilham — The “Medicine Hunter” on Fox News — about this subject (it starts with “Coffee vs. Tea: Do your homework, Fox News” and continues with “Chris Kilham Responds“).
Fermentation and oxidation are closely related processes. That’s certainly true. But oxidation is the aerobic process that is used in the production of black and oolong tea, and fermentation is the anaerobic process that’s used in the production of pu-erh tea. Using the word “fermentation” to describe the processing of black tea may fit with a lot of (non-chemist) tea industry writers, but it makes it difficult to explain what real fermented tea is.
Precision matters
In chatting with friends, imprecise use of words doesn’t matter. If someone asks what kind of tea you want and you respond, “chamomile,” it’s perfectly clear what you want. But you’re an industry reporter, medical writer, or marketing copywriter, your job is to communicate unambiguously to your readers. Using the most correct terminology in the right way is a great way to do that.
Book Review: 20,000 Secrets of Tea

I read a lot about tea (what a surprise, eh?), and try to carry a decent selection of tea books in my bookstore. When somebody recommended the book 20,000 Secrets of Tea: The Most Effective Ways to Benefit from Nature’s Healing Herbs by Victoria Zak, I decided to give it a look. I confess I was put off by the subtitle, because it sounds more like a book of herbal medicine than a book about tea. Then I flipped the book over and took a look at the back cover. There I saw this:
“An Ancient Chinese Legend: Once there was a man who knew 100,000 healing properties of herbs. He taught his son 80,000 secrets. On his deathbed, he told his son to visit his grave in five years, and there he would find the other 20,000 secrets. When the son went to his father’s grave, he found, growing on the site, the tea shrub…”
Okay, that’s more promising. Especially this line in the next paragraph: “A simple cup of tea not only has the power to soothe and relax but to deliver healing herbal agents to the bloodstream more quickly than capsules, tinctures, or infusions.” That line indicates that they know the difference between tea and infusions/tisanes, and that this book is going to be about tea.
Oh, my, was I wrong.
Page one starts out with a description of the legend of the origin of tea. Chapter one continues on, repeating the story from the back cover and then providing some of the history of tea as a drink. Within five pages, it has transitioned to herbal infusions, and that’s pretty much the end of discussion of the tea plant (Camellia sinensis).
I flipped through the next 220 pages looking for more information about tea (after all, the next 20,000 secrets are all about the tea shrub, right?) and I all found was descriptions of various herbs along with multitudinous health claims about each (more on that in a moment).
I went to the index looking for tea. The index is 15 pages long, normally a good sign in a reference book. Under “tea” I found reference to pages 1-4, mentioned above. Under Camellia sinensis, nothing. Flipping through the alphabetical collection of herbs, tea isn’t even listed. I checked under “black tea” and found a two-page spread in the middle titled “Green, Oolong, Black: the legendary teas.”
Zak begins by repeating the origin legend from page 1, and then proceeds to talk about fermentation (none of those teas are fermented, although black and oolong are oxidized) and rates the three styles in order of “medicinal strength: (green, then oolong, then black). Nowhere does she mention white or pu-erh tea, and nowhere does she define what “medicinal strength” actually means. Obviously, when there’s so little information, it leads to gross overgeneralization. When you use up that little bit of space with statements like “Green tea’s polyphenols are powerful antioxidants are reputed to be two hundred times stronger than vitamin E. It has anticancer catekins (sic), which protect the cells from carcinogens, toxins, free radical damage, and help to keep radioactive strontium 90 out of the bones,” there’s no room left to describe the differences between tea styles, how to properly steep a cup, or any of the other subjects that I expected this whole book to be about.
Incidentally, none of those rather incredible health claims are footnoted, no studies are cited, and no backup data is provided.
All in all, this book is tailor-made for herbalists — especially those that don’t worry much about the scientific basis of their health claims — but pretty well useless for tea enthusiasts.
Tea and caffeine part III: Decaf and low-caf alternatives

This article is the second of a three-part series.
Part I: What is caffeine?
Part II: Exploding the myths
Part III: Decaf and low-caf alternatives
So you’ve decided you like tea, but you really don’t want (or can’t have) the caffeine. What are your alternatives?
Well, first there’s decaf tea. As Part I of this series explained, decaffeination processes don’t remove 100% of the caffeine, so this is a reasonable alternative if you want less caffeine, but not if you want none at all. There’s another problem with switching to decaf: the selection of high-quality decaffeinated tea is — let’s just say, limited.
It’s easy to find a decaf Earl Grey or a decaf version of your basic Lipton-in-a-bag. But if your tastes run more to sheng pu-erh, sencha, dragonwell, lapsang souchong, silver needle, Iron Goddess of Mercy, or organic first-flush Darjeeling, you have a problem.
You can try the “wash” home-decaffeination method, but I explained a couple of days ago why that process is overrated. You’re likely to be able to remove 20% or so of the caffeine that way, but that’s about it.
Another alternative is simply to brew weaker tea and/or use more infusions. Let’s do the math for an example. Assume you’re a big fan of an oolong that contains 80 mg of caffeine in a tablespoon of leaves, and you drink four cups of tea per day.
If you use a fresh tablespoon of leaves for each cup, and you steep it for three minutes, you will be extracting about 42% of the caffeine in each cup, which equals 34 mg per cup, or a total of 136 mg of caffeine for the day. If you shorten your steep time to two minutes, the extraction level drops to about 33% (total of 106 mg). Alternatively, you could use the leaves twice each time, so you’re extracting about 63% of the caffeine, but using a total of half as many leaves (total of 101 mg). Or, if you don’t mind significantly weaker tea, just use 1-1/2 teaspoons of leaves instead of a full tablespoon. Half the leaves means half the caffeine (total of 68 mg).
No caffeine at all
If you look through the selection of teas in a health-food store, you’ll notice that most of them have no tea at all, and the vast majority of those non-tea drinks have no caffeine. The problem is that chamomile for a tea drinker is like Scotch to a wine drinker; it’s just not the same.
There are a couple of beverages, however, that are somewhat similar to tea. Both come from South Africa and both are naturally caffeine-free.
Rooibos is often called “red bush” in the United States because the way it’s usually prepared leaves a deep red infusion. Typically, rooibos is oxidized (not fermented) like a black tea. It can also be prepared more like a green tea. I blogged about green rooibos last August if you’d like to know more about it.
North American news shows, along with people like Oprah and Dr. Oz, have been singing the praises of rooibos lately, bringing it more into the mainstream awareness. It is very high in antioxidants and much lower in tannins than a black tea. Unfortunately, there isn’t a lot of independent research published about it yet, so many of the claims can’t really be backed up. The one that can be backed is that it has no caffeine and it tastes kind of like black tea (green rooibos is a bit grassy with malty undertones, more like a Japanese steamed green tea with a touch of black Assam).
Honeybush, like rooibos, grows only in South Africa. Also like rooibos, it is naturally caffeine-free and can be prepared either as a red or a green “tea.” When blooming, the flowers smell like honey, and honeybush tends to be somewhat sweeter than rooibos. Honeybush isn’t nearly as well-known as rooibos in the U.S., and the green version is very hard to find. I’ve found that if you want a flavored honeybush, citrus complements it very well. My “Hammer & Cremesickle Red” is the most popular honeybush blend in our tea bar (here is a blog post about it, and you can find it on the store website here).
A blended approach
If you like the idea of reducing your caffeine intake, but you don’t like the idea of a weaker tea (as I described above) or switching to rooibos or honeybush, you might want to consider blending. If you mix your tea half-and-half with something containing no caffeine, then you can still brew a strong drink, but get only half the caffeine from it. Combine that with the other tricks, like taking two infusions, and you can cut it even farther.






















 Legend says that tea originated in China in 2737 B.C., over 100 years before the first Egyptian pyramid was built. In this first stop on our
Legend says that tea originated in China in 2737 B.C., over 100 years before the first Egyptian pyramid was built. In this first stop on our 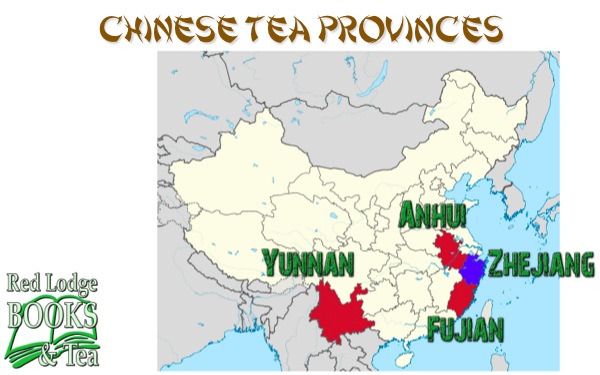











Complicated drinks, education, and consistency
Jul 7
Posted by Gary D. Robson
Is there some particular tea concoction that’s “your” tea drink? Is it something complicated? You’ll hear people every day in Starbucks ordering coffees that take twenty words to describe, but we don’t run in to that much in the tea bar … yet.
Why is it that more coffee drinkers than tea drinkers tend to be like the guys in this PVP Online comic? I think it’s a matter of education and consistency.
Most of our regulars at the tea bar are like me: they order something different each time they come in. I may go through phases where I drink nothing but malty Assam for a few days, but then I’m back to switching it up. I also drink different tea in the morning than I do in the afternoon or evening. Of course, I’m also that annoying guy that will go into a bar four times, order something completely different each time, and then ask for my “regular” on the fifth visit.
We do have some regulars that are consistent, but their drinks tend to be simple: a cup of sencha, Scottish breakfast with a touch of milk, or iced mango oolong. As people learn the menu and zero in on what they like, that is beginning to change a bit, though.
Amber is from the South. She likes her tea sweet, and she loves boba tea (a.k.a. “bubble tea”). I finally put the “Amber special” on the menu so she didn’t have to describe her boba tea made with Cinnamon Orange Spice tea, vanilla soy milk, and triple the usual sweet syrup.
Phyllis isn’t much of a tea fan, but she found herself drawn to Hammer & Cremesickle Red, which is a rooibos/honeybush blend. She likes it prepared as a latte with frothed 2% milk and a bit of honey.
Starbucks has dramatically changed coffee culture, much as McDonald’s has changed restaurants (I’m going to catch grief for that one, I know, but keep reading). You can go into a McDonald’s in an unfamiliar city, and you know that Big Mac and fries will be just like the ones back home. Similarly, you can go into any one of 19,555 Starbucks franchises and be comfortable that your half-caf double-shot venti skinny hazelnut macchiato will taste just like it would from the franchise back home. They have taught the world their own terminology (education) and made sure that the drinks are prepared exactly the same at each franchise (consistency).
Let’s look at those two factors as they apply to tea:
Consistency
The world of tea is generally not a good place for consistency. Even for fans of a single type of tea, the options are legion. There are dozens of matchas, hundreds of oolongs, and each has its own unique flavor. My tea bar offers six types of milk (nonfat, 2%, whole, half-and-half, vanilla soy, and almond), where another may offer 1%, light soy, and whole. When I went into the tea business’ closest thing to a national chain (Teavana – you can read about my visit here), they didn’t offer milk at all. You may go into one tea shop that has a hundred Chinese green and white teas and an English tea shop that has only black teas.
There’s a strong parallel to be drawn here with independent bookstores and big chains. You can find exactly the same books at a Barnes & Noble in Austin, Texas as you’d find in San Francisco, Denver, or New York. On the other hand, two indie bookstores a block apart can offer completely different experiences.
Tea aficionados revel in this. I enjoy wandering into a tea shop that has dozens of different pu-erhs available and tasting something I’ve never had before, even though I know the odds of finding that 1935 Double Lions Tongqing Hao anywhere else are close to zero (and the odds of being able to afford it are similar).
Tea shops can help a lot with this problem by proper labeling and by knowing the products well enough to compare our wares with popular brands from elsewhere. If someone walks into my shop that likes Constant Comment, I can guide them to my closest loose-leaf blend (that would be the aforementioned Cinnamon Orange Spice). If someone buys a mountain-grown Wuyi oolong in my shop, the next tea shop they visit should be able to give them something with a similar flavor profile.
Consumers can help by asking questions. If I have a breakfast tea I enjoy, I’ll ask the shopkeeper what’s in the blend. Then I’ll know to ask for an Assam/Tanzanian black breakfast tea blend next time I want something similar. I watch (or ask) how much leaf they use and what temperature the water is. Again, if I don’t know how they brewed it, I can’t ask for it to be prepared that way next time.
Education
The tea industry is where coffee and wine were a few decades ago. The average person has no idea what the difference is between a green tea and a white tea, but they know the difference between Merlot and Chardonnay. Tea people need to focus on education the same way wine and coffee people have done.
Educating customers is a bad thing for the mediocre shops. The more people learn about tea, the less likely they are to buy lower-grade products, and the less likely they are to buy from people who don’t know what they’re talking about. Once the person who’s been buying pre-sweetened chai from a box tastes fresh-brewed chai, they won’t be switching back.
On the other hand, education is a great thing for consumers and for good tea shops.
The more you know as a consumer, the better you’re able to find what you like and recognize the good products (and good prices). Educated consumers will frequent the better shops, and spend more money there, benefiting both the shop and the customer.
Share this:
Posted in Brewing
2 Comments
Tags: boba tea, chai, coffee, consistency, Constant Comment, education, McDonald's, PVP Online, Scott Kurtz, Starbucks, tea, wine